Other Windows Resolvers
Since you probably have hosts running older versions of Windows on your network, it’s helpful to know how these older resolvers behave, too.
Windows 95
Windows 95 includes its own TCP/IP stack with a DNS resolver. In fact, Windows 95 actually includes two TCP/IP stacks: one for TCP/IP over LANs and another for TCP/IP over dial-up connections. To get to the main DNS configuration panel, go to the Control Panel, then select Network. Select TCP/IP, then click the Properties button. This brings up a new dialog, which looks similar to the one in Figure 6-10. Choose the tab labeled DNS Configuration.
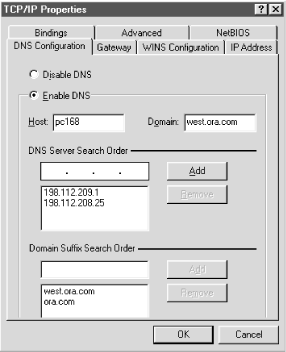
Figure 6-10. Resolver configuration under Windows 95
Configuration using this panel is fairly self-explanatory: first select Enable DNS to turn on DNS resolution, then fill in the PC’s hostname (in this case, the first label of its domain name) in the Host field and the local domain name (everything after the first dot) in the Domain field. Add the IP addresses of up to three name servers you want to query, in the order in which you want to query them, under DNS Server Search Order. Finally, fill in the domain names in the search list under Domain Suffix Search Order in the order in which you want them appended. If you leave out the Domain Suffix Search Order, the Windows 95 resolver derives one from the local domain name in the same way a Windows 2000 resolver does: ...
Get DNS on Windows 2000, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

