4.5. Comparison with infrared thermography
To demonstrate the thermo-inductive method’s potential, a comparative study with classical infrared thermography is conducted. The comparison will be done for the case of an inspection often found in the aeronautical industry. In this sector, one of the most common flaws is microcracks for aluminum plates. This type of imperfection is produced, by example, in pre-riveting drilling operations in the assembly phase.
Aluminum, like steel, is characterized by a high thermal diffusivity and thus requires a very short sampling time and an infrared camera with a sufficiently high acquisition time. In this case, the simulation parameters will be a sampling time of 5 ms for an acquisition time of tacq =5 s in order to have the thermal transient state.
4.5.1. Studied setup
Figure 4.35 shows the setup proposed for the inspection of the aluminum plate. It consists of the induction generator, the inductor, the infrared camera, and the inspected plate.
Figure 4.35. Schematic of the studied setup
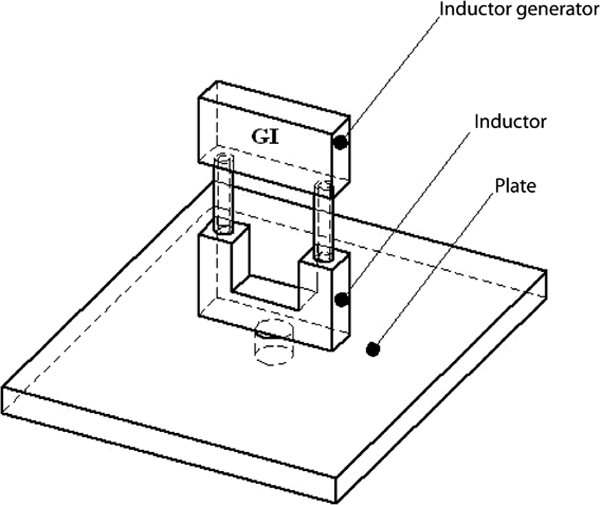
The thermo-inductive method was simulated for an aluminum plate whose principal dimensions are given in Figure 4.36. It consists of a pierced aluminum plate with a lateral flaw. The aluminum’s electromagnetic and thermal characteristics are given in Table 4.1.
A design and characterization study, similar to the study developed in the case of ferromagnetic materials, ...
Get Electrothermics now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

