The Life Cycle of a Stateless Session Bean
The life cycle of a stateless session bean is very simple. It only has two states: Does Not Exist and Method-Ready Pool . The Method-Ready Pool is similar to the instance pool used for entity beans. This is an important difference between stateless and stateful session beans; stateless beans define instance pooling in their life cycle and stateful beans do not.[29] Figure 11-1 illustrates the states and transitions a stateless session bean instance goes through in its lifetime.
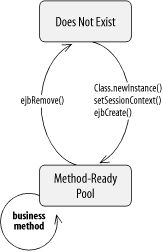
Figure 11-1. Stateless session bean life cycle
Does Not Exist
When a bean is in the Does Not Exist state, it is not an instance in the memory of the system. In other words, it has not been instantiated yet.
The Method-Ready Pool
Stateless bean instances enter the Method-Ready Pool as the container needs them. When the EJB server is first started, it may create a number of stateless bean instances and enter them into the Method-Ready Pool. (The actual behavior of the server depends on the implementation.) When the number of stateless instances servicing client requests is insufficient, more can be created and added to the pool.
Transitioning to the Method-Ready Pool
When an instance transitions from the Does
Not Exist state to the Method-Ready Pool, three operations are
performed on it. First, the bean instance is instantiated by invoking
the Class.newInstance( ) method ...
Get Enterprise JavaBeans, Fourth Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

