Chapter 9. Fast Ethernet Twisted-PairMedia System (100BASE-TX)
The 100BASE-TX twisted-pair media system is the most widely used Fast Ethernet media type. The 100BASE-TX standard is based on the twisted-pair specifications first developed for the FDDI TP-PMD (Twisted-Pair Physical Medium Dependent) standard. The system operates over two pairs of twisted-pair wires: one pair to receive data signals and the other pair to transmit data signals.
This chapter describes the signaling and media components used in the 100BASE-TX system. We also describe how a station is connected to a 100BASE-TX segment, and provide the basic configuration guidelines for a single segment.
100BASE-TX Signaling Components
The following signaling components may be used in the 100BASE-TX system to send and receive signals:
Ethernet interface with a built-in 100BASE-TX transceiver.
Medium-Independent Interface (MII).
External 100BASE-TX transceiver, also called a physical layer device (PHY).
100BASE-TX Ethernet Interface
A 100BASE-TX interface may be equipped with a built-in 100BASE-TX transceiver used to make a direct connection to the twisted-pair segment. If the interface is equipped with a 40-pin MII connector, external transceivers can be used. Figure 9.1 shows a network interface card designed to be installed in a desktop computer.
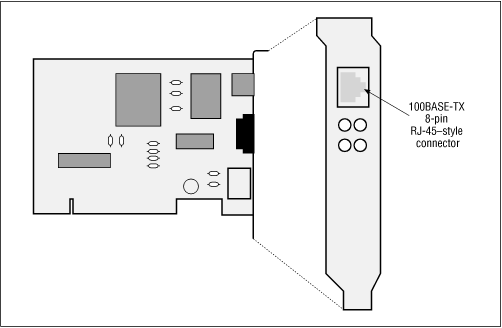
Figure 9.1. 100BASE-TX Ethernet interface
The card is equipped with an RJ-45-style ...
Get Ethernet: The Definitive Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

