3.7 Radio Network Mobility Management
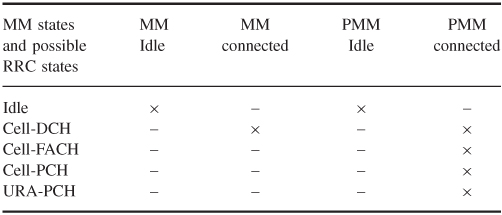
Depending on the MM state of the core network, the radio network can be in a number of different RRC states. How the mobility management is handled in the radio network depends on the respective state. Table 3.5 gives an overview of the MM and PMM states in the core network and the corresponding RRC states in the radio network.
Table 3.5 Core network and radio network states
3.7.1 Mobility Management in the Cell-DCH State
For services like voice or video communication it is very important that little or no interruption of the data stream occurs during a cell change. For these services, only the Cell-DCH state can be used. In this state, the network constantly controls the quality of the connection and is able to redirect the connection to other cells if the subscriber is moving. This procedure is called handover or handoff.
A handover is controlled by the Radio Network Controller and triggered based on measurement values of the quality of the uplink signal measured by the base station and measurement reports on downlink quality sent by the mobile device. Measurement reports can be periodic or event triggered. Different radio network vendors use different strategies for measurement reporting. Unlike in GSM where only the signal strength, referred to as Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI), is used for the decision, UMTS needs additional ...
Get From GSM to LTE: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile Broadband now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

