Data Management
DM is the structured organization of information and resources. DAMA defines DM as “the development and execution of architectures, policies, practices, and procedures that properly manage the full data lifecycle needs of an enterprise” (www.dama.org/i4a/pages/index.cfm?pageid=3339). This group is setting market practice standards. Exhibit 14.1 represents DAMA’s framework for best practices in DM. The application in audit and detection could incorporate these components when designing a process to collect and maintain audit data.
Exhibit 14.1 Data Management Functions
Source: Data Management Association (DAMA; http://www.dama.org). Copyright 2007 DAMA International–All Rights Reserved.
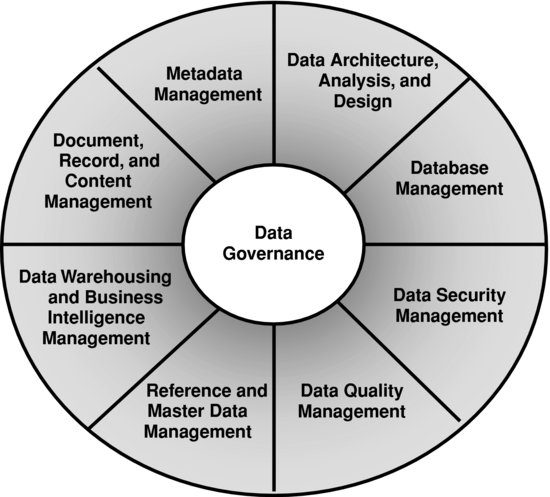
The model given in Exhibit 14.1 can be used as a guide in developing data models to be used in the audit and detection of healthcare fraud. The category of Document, Record, and Content Management is seen as an opportunity to identify your list of data elements to be collected within your audit scope. For example, are you looking only at the internal communications of a provider? Will you be analyzing internal and external data elements between an employer and a payer? Under Data Architecture, Analysis, and Design is, in essence, how your data will be structured, organized, and processed. Database Management involves specific policy and procedure for the application, execution, update, ...
Get Healthcare Fraud: Auditing and Detection Guide, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

