How IGRP Works
Since IGRP is such a close cousin of RIP, we will not repeat the details of how DV algorithms work, how updates are sent, and how route convergence is achieved. However, because IGRP employs a much more comprehensive metric, I’ll discuss the IGRP metric in detail. I’ll begin this discussion with AS numbers.
IGRP Autonomous System Number
Each IGRP process requires an autonomous system number:
router igrp autonomous-system-numberThe AS number allows the network administrator to define routing domains; routers within a domain exchange IGRP routing updates with each other but not with routers in different domains. Note that in the context of IGRP the terms “autonomous system number” and “process ID” are often used interchangeably. Since the IGRP autonomous system number is not advertised to other domains, network engineers often cook up arbitrary process IDs for their IGRP domains.
Let’s say that TraderMary created a subsidiary in Africa and that the new topology is as shown in Figure 3-2.
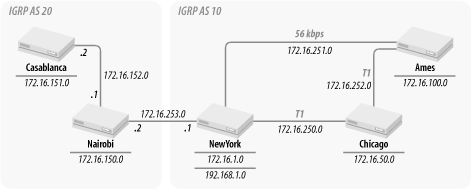
Figure 3-2. TraderMary’s U.S. and African networks
Note that IGRP is running in the U.S. and Africa with AS numbers of 10 and 20, respectively. The U.S. routers now exchange IGRP routes with each other, as before, and the routers Nairobi and Casablanca exchange IGRP updates with each other. IGRP updates are processed only between routers running the same AS number, so NewYork and Nairobi ...
Get IP Routing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

