Now I want to show you two more handler classes that SAX offers. Both
of these interfaces are no longer part of the core SAX distribution,
and are located in the org.xml.sax.ext
package
to indicate they are extensions to SAX. However, most parsers (such
as Apache Xerces) include these two classes for use. Check your
vendor documentation, and if you don’t have these classes, you
can download them from the SAX web site. I warn you that not all SAX
drivers support these extensions, so if your vendor doesn’t
include them, you may want to find out why, and see if an upcoming
version of the vendor’s software will support the SAX
extensions.
The first of these two handlers is the most useful:
org.xml.sax.ext.LexicalHandler
.
This handler provides methods that can receive notification of
several lexical events such as comments, entity declarations, DTD
declarations, and CDATA sections. In
ContentHandler, these lexical events are
essentially ignored, and you just get the data and declarations
without notification of when or how they were provided.
This is not really a general-use handler, as most applications
don’t need to know if text was in a CDATA
section or not. However, if you are working with an XML editor,
serializer, or other component that must know the exact
format of the input document, not just its
contents, the LexicalHandler can really help you
out. To see this guy in action, you first need to add an import
statement for org.xml.sax.ext.LexicalHandler to
your SAXTreeViewer.java source
file. Once that’s done, you can add
LexicalHandler to the
implements clause in the nonpublic class
JTreeContentHandler in that source file:
class JTreeContentHandler implements ContentHandler, LexicalHandler {
// Callback implementations
}By reusing the content handler already in this class, our lexical
callbacks can operate upon the JTree for visual
display of these lexical callbacks. So now you need to add
implementations for all the methods defined in
LexicalHandler. Those methods are as follows:
public void startDTD(String name, String publicID, String systemID)
throws SAXException;
public void endDTD( ) throws SAXException;
public void startEntity(String name) throws SAXException;
public void endEntity(String name) throws SAXException;
public void startCDATA( ) throws SAXException;
public void endCDATA( ) throws SAXException;
public void comment(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException;To get started, let’s look at the first lexical event that
might happen in processing an XML document: the start and end of a
DTD reference or declaration. That triggers the startDTD( ) and endDTD( ) callbacks, shown here:
public void startDTD(String name, String publicID,
String systemID)
throws SAXException {
DefaultMutableTreeNode dtdReference =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode("DTD for '" + name + "'");
if (publicID != null) {
DefaultMutableTreeNode publicIDNode =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Public ID: '" +
publicID + "'");
dtdReference.add(publicIDNode);
}
if (systemID != null) {
DefaultMutableTreeNode systemIDNode =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode("System ID: '" +
systemID + "'");
dtdReference.add(systemIDNode);
}
current.add(dtdReference);
}
public void endDTD( ) throws SAXException {
// No action needed here
}This adds a visual cue when a DTD is encountered, and a system ID and
public ID if present. Continuing on, there are a pair of similar
methods for entity references, startEntity( ) and
endEntity( ). These are triggered before and after
(respectively) processing entity references. You can add a visual cue
for this event as well, using the code shown here:
public void startEntity(String name) throws SAXException {
DefaultMutableTreeNode entity =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Entity: '" + name + "'");
current.add(entity);
current = entity;
}
public void endEntity(String name) throws SAXException {
// Walk back up the tree
current = (DefaultMutableTreeNode)current.getParent( );
}This ensures that the content of, for example, the
OReillyCopyright entity reference is included
within an “Entity” tree node. Simple enough.
Because the next lexical event is a CDATA section,
and there aren’t any currently in the contents.xml document, you may want to make
the following change to that document (the CDATA
allows the ampersand in the title element’s
content):
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE book SYSTEM "DTD/JavaXML.dtd">
<!-- Java and XML Contents -->
<book xmlns="http://www.oreilly.com/javaxml2"
xmlns:ora="http://www.oreilly.com"
>
<title ora:series="Java"><![CDATA[Java & XML]]></title>
<!-- Other content -->
</book>With this change, you are ready to add code for the
CDATA callbacks. Add in the following methods to
the JTreeContentHandler class:
public void startCDATA( ) throws SAXException {
DefaultMutableTreeNode cdata =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode("CDATA Section");
current.add(cdata);
current = cdata;
}
public void endCDATA( ) throws SAXException {
// Walk back up the tree
current = (DefaultMutableTreeNode)current.getParent( );
}This is old hat by now; the title element’s content now appears
as the child of a CDATA node. And with that, only
one method is left, that which receives comment notification:
public void comment(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException {
String comment = new String(ch, start, length);
DefaultMutableTreeNode commentNode =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Comment: '" + comment + "'");
current.add(commentNode);
}This method behaves just like the characters( )
and ignorableWhitespace( ) methods. Keep in mind
that only the text of the comment is reported to this method, not the
surrounding <!— and —> delimiters. With these
changes in place, you can compile the example program and run it. You
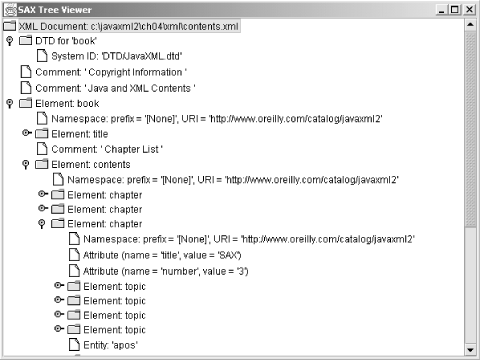
should get output similar to that shown in Figure 4-3.
You’ll notice one oddity, though: an entity named
[dtd]. This occurs anytime a
DOCTYPE declaration is in place, and can be
removed (you probably don’t want it present) with a simple
clause in the startEntity( ) and
endEntity( ) methods:
public void startEntity(String name) throws SAXException {
if (!name.equals("[dtd]")) {
DefaultMutableTreeNode entity =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Entity: '" + name + "'");
current.add(entity);
current = entity;
}
}
public void endEntity(String name) throws SAXException {
if (!name.equals("[dtd]")) {
// Walk back up the tree
current = (DefaultMutableTreeNode)current.getParent( );
}
}This clause removes the offending entity. That’s really about
all that there is to say about LexicalHandler.
Although I’ve filed it under advanced SAX, it’s pretty
straightforward.
The last handler to deal with is the
DeclHandler
.
This interface defines methods that receive notification of specific
events within a DTD, such as element and attribute declarations. This
is another item only good for very specific cases; again, XML editors
and components that must know the exact lexical structure of
documents and their DTDs come to mind. I’m not going to show
you an example of using the DeclHandler; at this
point you know more than you’ll probably ever need to about
handling callback methods. Instead, I’ll just give you a look
at the interface, shown in Example 4-6.
Example 4-6. The DeclHandler interface
package org.xml.sax.ext;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
public interface DeclHandler {
public void attributeDecl(String eltName, String attName,
String type, String defaultValue,
String value)
throws SAXException;
public void elementDecl(String name, String model)
throws SAXException;
public void externalEntityDecl(String name, String publicID,
String systemID)
throws SAXException;
public void internalEntityDecl(String name, String value)
throws SAXException;
}This example is fairly self-explanatory. The first two methods handle
the <!ELEMENT> and
<!ATTLIST> constructs. The third,
externalEntityDecl( ), reports entity declarations
(through <!ENTITY>) that refer to external
resources. The final method, internalEntityDecl( ), reports entities defined inline. That’s all there
is to it.
And with that, I’ve given you everything that there is to know about SAX. Well, that’s probably an exaggeration, but you certainly have plenty of tools to start you on your way. Now you just need to get coding to build up your own set of tools and tricks. Before closing the book on SAX, though, I want to cover a few common mistakes in dealing with SAX.
Get Java and XML, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.