Playing Sounds with javax.sound
To achieve more detailed control over the playback of sounds,
including the ability to skip to any specified spot in the sound and
control things such as volume and balance, we must use the Java Sound
API, which is a much lower-level API than the AudioClip interface. JavaSound consists of
the javax.sound.sampled package for
sampled audio and the javax.sound.midi package for MIDI-based audio. Example 17-3 demonstrates the
basic capabilities of these two packages. It loads a sound file
(sampled audio or MIDI) completely into memory and then displays a GUI
that allows you to play it. The GUI makes extensive use of the Swing
JSlider component, which allows you
both to select the playback position of the sound and to set things
such as the volume, balance, and tempo of the sound. The program
displays different controls for sampled audio files than it does for
MIDI files. Both GUIs are shown in Figure 17-1. You’ll notice that
the code is substantially different for sampled audio and MIDI files
as well.
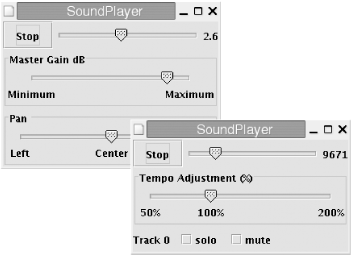
Figure 17-1. SoundPlayer playing sampled audio and MIDI files
A shortcoming of the SoundPlayer class is that it can only play
sampled audio files that use PCM encoding. ALAW and ULAW encoded files are not supported, nor are more complex compressed encodings, such as MP3. The JavaSound API attempts to directly mirror the capabilities of sound hardware, and ...
Get Java Examples in a Nutshell, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

