Chapter 8. Java Modifiers
Modifiers, which are Java keywords, may be applied to classes, interfaces, constructors, methods, and data members.
Table 8-1 lists the Java modifiers and their applicability.
|
Modifier |
Class |
Interface |
Constructor |
Method |
Data member |
|
Access modifiers | |||||
|
package-private |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
private |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
protected |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
public |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Other modifiers | |||||
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
|
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Access Modifiers
Access modifiers define the access privileges of classes, interfaces, constructors,
methods, and data members. Access modifiers consist of public,
private, and protected. If no modifier is
present, the default access of package-private is used.
Figure 8-1 illustrates the visibility of the
access modifiers, including the differences between classes that are public and package-private. Note that in
the figure, the modifiers refer to both data members and methods.
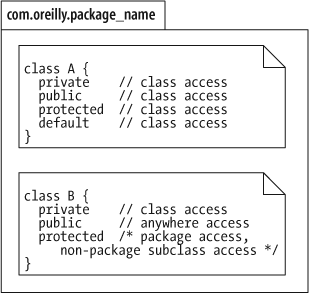
Table 8-2 provides details on the visibility when these access modifiers ...
Get Java Pocket Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

