Online Shopping
Now let’s look
at a more useful example: an online
shopping site. Besides showing you how the session and application
scopes can be used effectively in a larger
application, this example
also introduces many other useful tools. You’ll see a number of
generic custom actions you can use in your own applications, and
learn how to use the java.text.NumberFormat class
to format numbers.
The application consists of three pages. The main page lists all available products. Each product is linked to a product description page, where the product can be added to the shopping cart. A product is added to the shopping cart by a request processing page. The main page with the product list is then displayed again, but now with the current contents of the shopping cart as well, as shown in Figure 8.6.
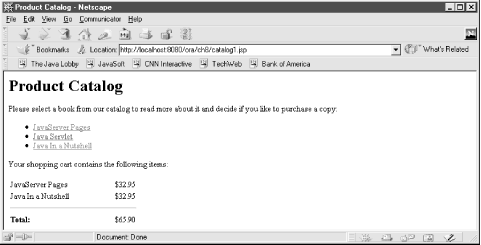
Figure 8-6. The product list and the contents of the shopping cart
Two beans are used to keep
track of the products: the
com.ora.jsp.beans.shopping.CatalogBean
contains all available products, and the
com.ora.jsp.beans.shopping.CartBean represents one
user’s shopping cart. Each product in the catalog is
represented by a
ProductBean
.
Tables Table 8.6, Table 8.7, and Table 8.8 show all the properties for the beans.
Table 8-6. Properties for com.ora.jsp.beans.shopping.CatalogBean
|
Property Name |
Java Type |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
productList |
com.ora.jsp.beans. shopping.ProductBean[] |
read ... |
Get Java Server Pages now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

