Chapter 19. Text 101
Swing
provides an extensive collection of classes for working with text in
user interfaces. In fact, there’s so much provided for working
with text, Swing’s creators placed most of it into its own
package:
javax.swing.text
. This package’s dozens of
interfaces and classes (plus the five concrete component classes in
javax.swing) provide a rich (and complex!) set of
text-based models and components. Over the course of the next six
chapters, we’ll cover each of these classes and interfaces in
detail. Figure 19.1 shows a very high-level view of
the structure of the Swing text components. The arrows in the figure
can be read as “knows about,” or “uses.”
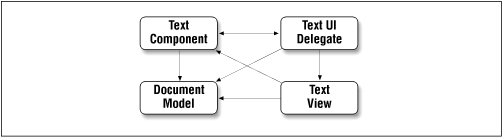
Figure 19-1. High-level view of the Swing text framework
The text content for any component is stored in a model object called
a Document. Chapter 20, and
Chapter 21, cover the complex Swing document model
in considerable detail. This model allows you to represent highly
structured text supporting multiple fonts and colors, and even
embedded Icons and Components.
Swing text components allow you to customize certain aspects of the
look-and-feel without much work. This includes the creation of custom
carets (cursor) and custom highlighting, as well as the definition of
custom key bindings, allowing you to associate
Actions with special key combinations. These
features are covered in Chapter 22.
As usual, each text component ...
Get Java Swing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

