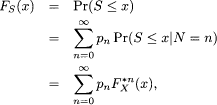9.3 The compound model for aggregate claims
Let S denote aggregate losses associated with a set of N observed claims X1, X2, …, XN satisfying the independence assumptions following (9.1). The approach in this chapter involves the following three steps:
Completion of the first two steps follows the ideas developed elsewhere in this text. We now presume that these two models are developed and that we only need to carry out numerical work in obtaining solutions to problems associated with the distribution of S.
The random sum
![]()
(where N has a counting distribution) has distribution function
where FX(x) = Pr(X ≤ x) is the common distribution function of the Xjs and pn = Pr(N = n). The distribution of S is called a compound distribution. In (9.3), FX*n(x) is the “n-fold convolution” of the cdf of X. It can be obtained as
![]()
and
The tail may then be written, ...
Get Loss Models: From Data to Decisions, 4th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.