IEEE 802.16m
The amendment for IEEE 802.16m describes extensive network architecture for Advanced IEEE 802.16 networks. With a refined separation between access and management network services, the IEEE 802.16m provides details for functional entities and interfaces. The IEEE 802.16m network reference model is shown in Figure 3.4.
Similar to the IEEE 802.16-2009, the standard's descriptions is constrained to the access network aspect. The scope of the IEEE 802.16m amendment spans the description for the Access Service Network (ASN) and the Advanced Mobile Subscriber (AMS). Detailed abstractions are provided for the Connectivity Service Network (CSN), which effectively oversees the higher layer management and connectivity functionalities of the IEEE 802.16m network, in addition to providing the required connectivity for the network's backbone.
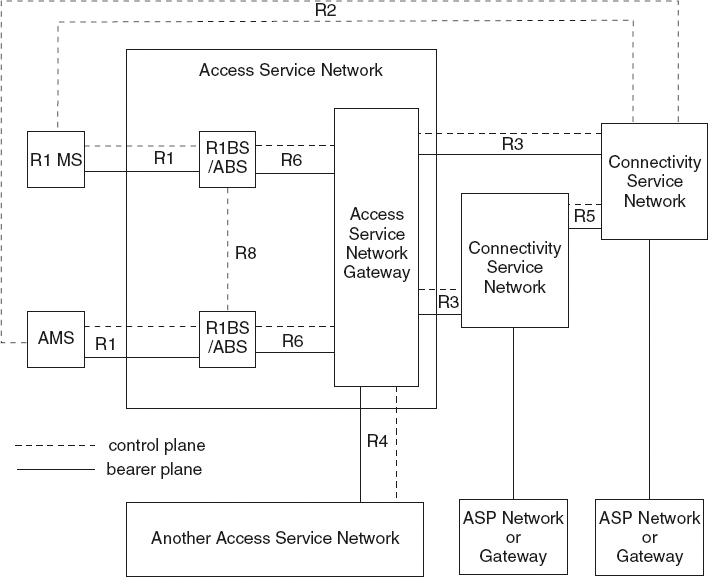
Figure 3.4 The IEEE 802.16m network reference model. Reproduced by permission of © 2009 IEEE.
Figure 3.5 shows the different deployment examples in 16m. The “purely” advanced network comprises Advanced Base Stations (ABSs) assuming control of the air interface, and through which AMSs (either directly or indirectly) connect to the ASN and CSN. An IEEE 802.16m network may also use Advanced Relay Stations (ARS) as in IEEE 802.16-2009. These can be either, tRSs or ntRSs, based on which centralized or distributed schedulers are used.
An IEEE 802.16m ...
Get LTE, LTE-Advanced and WiMAX: Towards IMT-Advanced Networks now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

