Mobility Management in IEEE 802.16-2009
Figure 7.1 shows the procedures involved in initiating and carrying out a handover. The standard does not specify how the handover decision should be made, nor does it mandate whether the decision should be made by the network or the MS. The standard, however, provides means for information acquisition by both the BS and the MS to make efficient decisions. The information acquired generally specifies the quality of the signal received by the MS from the various BS, but also information on the readiness of these BSs to support the MS's requirements.
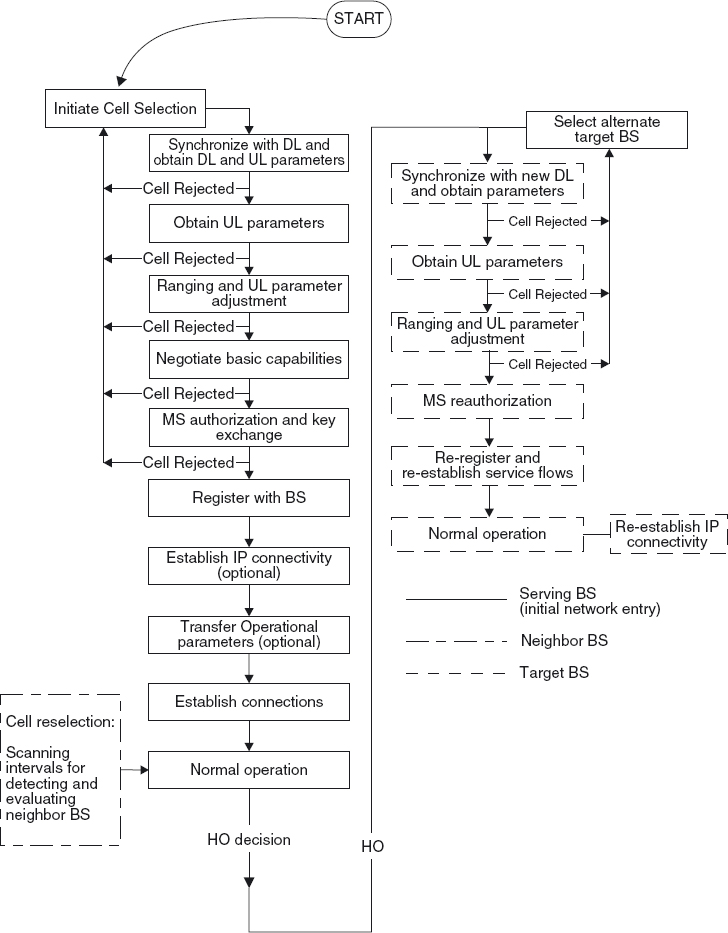
Figure 7.1 Flow chart for handover process. Reproduced by permission of © 2009 IEEE.
The procedures in the figure are almost identical to those of network entry and initialization, which were described previously in Chapter 5. To enhance service delivery for an already active call, the standard defined certain optimizations so as to accelerate the handover process. These optimizations are described on the next page. In addition, certain enhancements in the standard, such as seamless handover and macro-diversity handovers, will be outlined.
Acquiring Network Topology
A network topology means different things for the BS and the MS. A BS requires an understanding of the capabilities of its neighboring BS, and requires active communication links to these BS for various mobility management objectives, ...
Get LTE, LTE-Advanced and WiMAX: Towards IMT-Advanced Networks now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

