ActiveX Security
Java’s default security model runs untrusted code in a security sandbox. ActiveX’s default model (see Figure 11-3 later in this chapter) doesn’t run untrusted code, period! The defining question is how ActiveX determines what is untrusted code. In many cases, it doesn’t, you do. When you download an ActiveX control, Internet Explorer checks for the existence of a digital signature to verify its authorship. Depending on the browser’s security setting, you may then be asked (see Figure 11-1) to accept or deny the control’s downloading and execution.
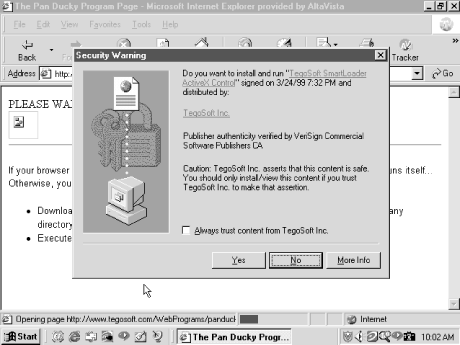
Figure 11-1. Internet Explorer ActiveX warning
As you are prompted to accept a new, signed control for the first
time, the browser will also allow you to accept every control signed
by the same author, if you check the Always trust content from box. If you do, future controls from the same author
or vendor, now considered trusted
publishers
, will not result in additional
notifications. They will download and execute without warning. This
is a lot of trust to give a vendor, so give it with due
consideration. Microsoft writes trusted publishers to the following
registry keys:
HKU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WinTrust\TrustedPublishers\SoftwarePublishing\TrustDatabase\0
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WinTrust\TrustedPublishers\SoftwarePublishing\TrustDatabase\0
A few sneaky controls have ignored ...
Get Malicious Mobile Code now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

