Introducing Windows Virtual PC
Despite the release of Windows 8, many organizations will continue to use Windows 7 for some time. As previously discussed, Windows Virtual PC is the Microsoft client virtualization solution for Windows 7, so this section takes a brief look at using Windows Virtual PC under Windows 7, as it also forms the foundation for both XP Mode and MED-V.
Windows Virtual PC runs on 32-bit or 64-bit processors and runs on all versions of Windows 7 Home Basic and above. Initially, Windows Virtual PC required the processor to support hardware-assisted virtualization, even though it is only a type 2 hypervisor, but an update released shortly after Windows Virtual PC was released removed that requirement.
Windows Virtual PC is available at http://www.microsoft.com/windows/virtual-pc/download.aspx and includes the update. Once installed, Windows Virtual PC is available from the Start menu, and virtual machines can be started and stopped through a new integration with Explorer, as shown in Figure 3-4.
Figure 3-4: Viewing and controlling virtual machines with Windows Virtual PC
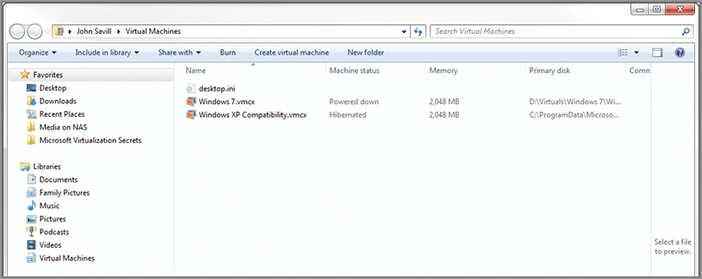
The virtual machines created with Windows Virtual PC can only have a single virtual processor assigned to them; and because only 32-bit guests can run in the VM, a maximum of 3.7GB of memory can be allocated. The guest operating systems supported by Windows Virtual PC are Windows XP SP3 and above, ...
Get Microsoft Virtualization Secrets now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

