10.4 LBS CLASSIFICATION
The examination of application domains like mobile marketing or mobile gaming is useful for giving people a general idea about the purposes, appearances, and benefits of LBSs, but it does not help in identifying the required functions that constitute a particular LBS. Examples of such functions are positioning methods, strategies for exchanging position data between the actors participating in the supply chain of an LBS, privacy mechanisms, or protocols. They should be arranged in a way that they can be reused for a broad range of different applications and tailored to their special requirements. Figure 10.3 gives an overview of the different criteria for classifying LBSs from a functional point of view. The criteria are explained and discussed below.
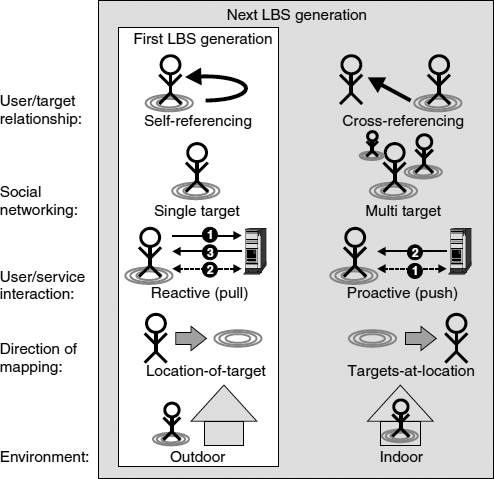
Figure 10.3 Functional classification of LBSs.
Self-referencing vs. cross-referencing LBSs. An important distinction has to be made concerning the roles the participants of an LBS adopt during its execution. Generally, it can be distinguished between the roles of the LBS user and the target. The LBS user is the person that requests and consumes the LBS. A target, on the other hand, is the individual to be located and tracked. In self-referencing LBSs, user and target are the same individual, that is, the user's location is processed for her own purposes. Typical examples are finder services, which show the user ...
Get Mobile Intelligence now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

