2 A Journey Through an Uncertain Reality
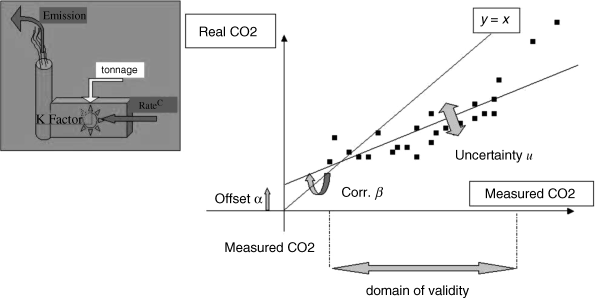
Simple examples will help one to grasp the scope of this book and the reader is also invited to refer to de Rocquigny, Devictor, and Tarantola (2008) which gathers a large number of recent real-scale industrial case studies. Look firstly at the domain of metrology. Knowing the value of a quantitative variable representing the state or performance of the system requires an observational device which inevitably introduces a level of measurement uncertainty or error. Figure 1 illustrates the measurement results from a given device as compared to the reference values given by a metrological standard (i.e. a conventionally ‘finer’ measurement). Uncontrollable dispersion remains even after the best calibration efforts, the first materialisation of uncertainty. Such uncertainty will need to be estimated and modelled in order to undertake, for instance, a risk assessment of an emission control system.
Figure 1 Metrological uncertainty in the CO2 emissions of an industrial process.
Within the field of natural phenomena, temporal or spatial variability is ubiquitous and has a number of impacts: natural aggressions or environmental constraints on settlements or the operation of industrial facilities. Figure 2 -up illustrates the year-to-year natural variability of maximal flows from a French river. Because of the well-known sensitivity to initial conditions, ...
Get Modelling Under Risk and Uncertainty: An Introduction to Statistical, Phenomenological and Computational Methods now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

