Chapter 17. Advanced Pointers
A race that binds
Its body in chains and calls them Liberty,
And calls each fresh link progress.
One of the more useful and complex features of C is its use of pointers. With pointers, you can create complex data structures like linked lists and trees. Figure 17-1 illustrates some of these data structures.
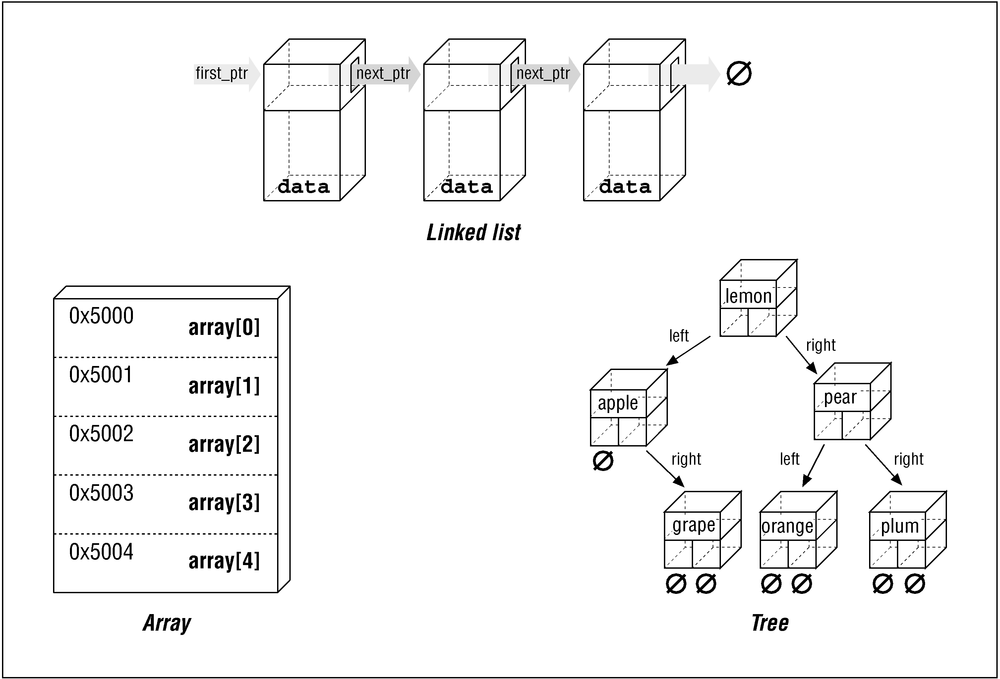 |
Up to now, all of our data structures have been allocated by the compiler as either permanent or temporary variables. With pointers, we can create and allocate dynamic data structures that can grow or shrink as needed. In this chapter, you will learn how to use some of the more common dynamic data structures.
Pointers and Structures
Structures can contain pointers, even a pointer to another instance of the same structure. In the following example:
struct node {
struct node *next_ptr; /* Pointer to the next node */
int value; /* Data for this node */
}the structure node is
illustrated in Figure 17-2.
This structure contains two fields, one named value, shown here as the section containing
the number 2. The other is a pointer to another structure. The field
next_ptr is shown as an
arrow.
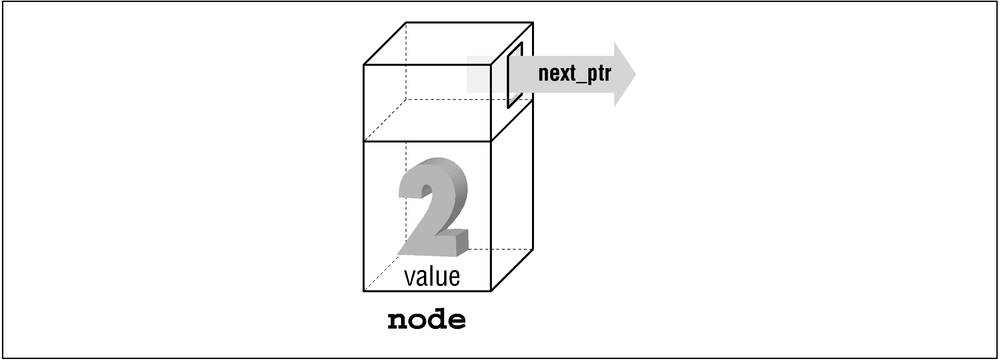 |
The question is: how do we create nodes? We could declare them
explicitly:
struct node *node_1; struct node ...
Get Practical C Programming, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

