1.2 DETERMINISTIC SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
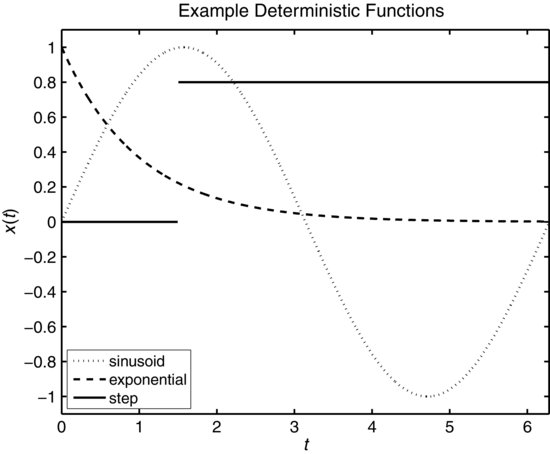
In engineering programs, students usually learn about signals and systems first in the time domain and then in the frequency domain. The focus is on deterministic signals such as those illustrated in Figure 1.19.
Figure 1.19 Examples of deterministic signals: sinusoid ![]() , exponential
, exponential ![]() , and step
, and step ![]() where u(t) is the unit-step function.
where u(t) is the unit-step function.
1.2.1 Continuous Time
Nonrandom signal x(t) is a function of continuous time ![]() . Consider the sinusoidal signal
. Consider the sinusoidal signal
(1.15) ![]()
shown in Figure 1.19 for ![]() where u(t) is the unit-step (Heaviside) function (see Appendix B). Radian frequency ω (radians/second) is related to ordinary frequency f in hertz (Hz) according to
where u(t) is the unit-step (Heaviside) function (see Appendix B). Radian frequency ω (radians/second) is related to ordinary frequency f in hertz (Hz) according to ![]() . For a particular ...
. For a particular ...
Get Probability, Random Variables, and Random Processes: Theory and Signal Processing Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

