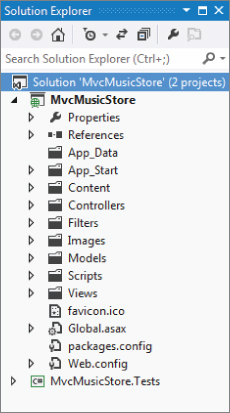
The MVC Application Structure
When you create a new ASP.NET MVC application with Visual Studio, it automatically adds several files and directories to the project, as shown in Figure 1.14. ASP.NET MVC projects created with the Internet application template have eight top-level directories, shown in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1: Default Top-Level Directories
| Directory | Purpose |
| /Controllers | Where you put Controller classes that handle URL requests |
| /Models | Where you put classes that represent and manipulate data and business objects |
| /Views | Where you put UI template files that are responsible for rendering output, such as HTML |
| /Scripts | Where you put JavaScript library files and scripts (.js) |
| /Images | Where you put images used in your site |
| /Content | Where you put CSS and other site content, other than scripts and images |
| /Filters | Where you put filter code. Filters are an advanced feature, discussed in Chapter 14. |
| /App_Data | Where you store data files you want to read/write |
| /App_Start | Where you put configuration code for features like Routing, Bundling, and Web API |
Get Professional ASP.NET MVC 4 now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.