Managed Providers
The previous examples used one of the managed providers initially available with ADO.NET: the SQL managed provider. The SQL managed provider is optimized for Microsoft SQL Server, but it is restricted to working with SQL Server databases. The more general solution is the OLE DB managed provider, which connects to any OLE DB provider, including Microsoft Access and MSDE (which is provided for free).
You can rewrite Example 19-1 to work with the Bugs database using Microsoft Access rather than Microsoft SQL Server with just a few small changes. First, you need to create a new Access database. Name the new database SimpleBugListBoxAccessDB. Example 19-6 assumes you will save your database to the root directory on your C drive, but you may save it anywhere else that is convenient for you as long as you adjust the connection string accordingly.
Use the File → Get External Data → Import menu option in Access to import the data from the SQL database. This will create tables in Access that reflect the structure and content of the data in the SQL database. Notice that the Bugs database is now named dbo_Bugs in Access.
Create a new ASP Application project named SimpleBugListboxAccessCS, and once again drag a ListBox onto the form, resize it, and name it lbBugs. Copy the code from Example 19-2, but make the following changes:
Change the connection string to:
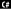
string connectionString ...
Get Programming .NET Windows Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

