5.1. The scattering matrix S of a two-port network is given as
5.91 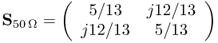
The port reference impedance is Z0 = 50 Ω.
a. Determine the properties of the network: is it matched? Is it reciprocal? Is it symmetric? Is is loss-less? Give reasons for your answers.
b. Calculate the reflection loss (RL) and the insertion loss (IL).
c. Renormalize the scattering matrix to a new port reference impedance of Z0, new = 100 Ω.
5.2. With a vector network analyser we measure a reflection coefficient of
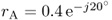
at the input terminals of an antenna. Port reference impedance is
Z0 = 50 Ω.
a. Determine the input impedance ZA of the antenna.
We connect the antenna to a transmission line with a characteristic impedance of Z0L = 75 Ω. The incident active power on the transmission line is set to Pa1 = 1 W.
a. Calculate the reflected power Pb1 at the antenna terminals and the power Pacc that is accepted by the antenna.
5.3. Determine the scattering matrices of the two-port networks given in
Figure 5.24. The port reference impedance is
Z0 for all ports.
5.4. Figure 5.25 shows a cascade connection of three two-port networks. An unknown ...
![]()
