7.3 Mathematical Treatment of the Hertzian Dipole
The Hertzian dipole is an infinitely small radiating current element. The electromagnetic field of this theoretical antenna can be calculated mathematically in closed form [2, 9, 10]. The current distribution on practical antennas—especially wire antennas—can be represented by Hertzian dipole elements. Furthermore, essential antenna parameters can be illustrated and understood from the example of the Hertzian dipole.
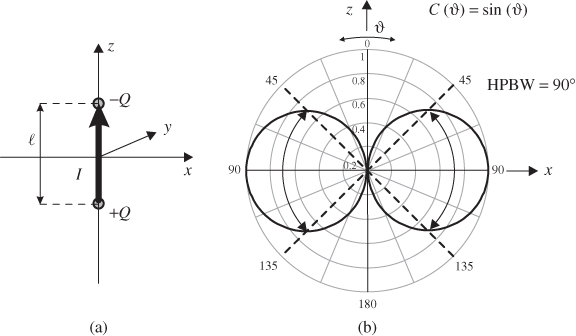
Figure 7.8a shows the geometry of the Hertzian dipole. A time-dependent homogeneous current I flows along the z-axis. The length ![]() of the element approaches zero, but the product of current and length I
of the element approaches zero, but the product of current and length I![]() shall be finite. Time-dependent charges Q and −Q exist at the ends of the current element. We consider harmonic time-dependency and apply complex phasor notation.
shall be finite. Time-dependent charges Q and −Q exist at the ends of the current element. We consider harmonic time-dependency and apply complex phasor notation.
Figure 7.8 Hertzian dipole: (a) linear element with uniform current and (b) vertical radiation pattern.
In order to calculate the electric field strength ![]() and the magnetic field strength we use the magnetic vector potential as an auxiliary quantity. So, the mathematical ...
and the magnetic field strength we use the magnetic vector potential as an auxiliary quantity. So, the mathematical ...
Get RF and Microwave Engineering: Fundamentals of Wireless Communications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

