Chapter 14: Differential Pairs
14.1 Fundamentals of Differential Pairs
14.1.1 Topology and Definition of a Differential Pair
For the integrity of description for the single-ended block and the differential pair, let us copy Figure 13.1, Figure 13.2, and equations (13.1) to (13.4) to this section and relabel them as Figure 14.1, Figure 14.2, and equations (14.1) to (14.4), respectively.
14.2 ![]()
14.3 ![]()
It should be reiterated that both differential branches are expected to be symmetrical to each other in all aspects, including their values, sizes, configurations, and layouts.
Figure 14.1 Typical single-ended block. (a) A bipolar single-ended block. (b) A MOSFET single-ended block.
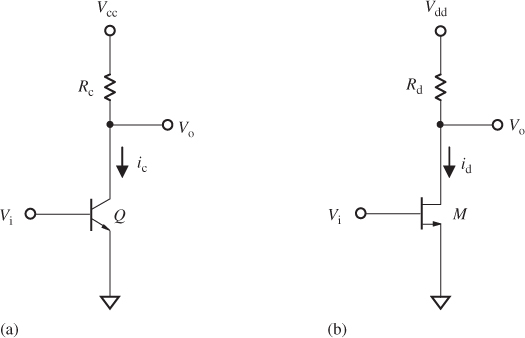
Figure 14.2 Typical differential pair. (a) A bipolar differential pair. (b) A MOSFET differential pair.
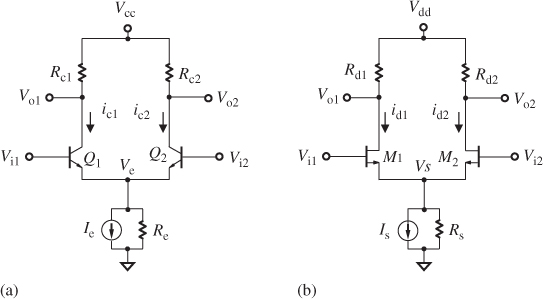
In order to clarify the DC and AC characters of the differential pair, it is better to denote the ...
Get RF Circuit Design, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

