3.1 Baseline Saliency Model for Images
The baseline salience (BS) model (referred to as Itti's model in some literature) refers to the classical bottom-up visual attention model for still images, proposed by Itti et al. [2], and its variations have been explored in [3–5, 11, 12]. Their core modules are shown in Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1 The core of bottom-up visual attention models [2, 5] in the spatial (pixel) domain. © 1998 IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from L. Itti, C. Koch, E. Niebur, ‘A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis’, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Nov. 1998
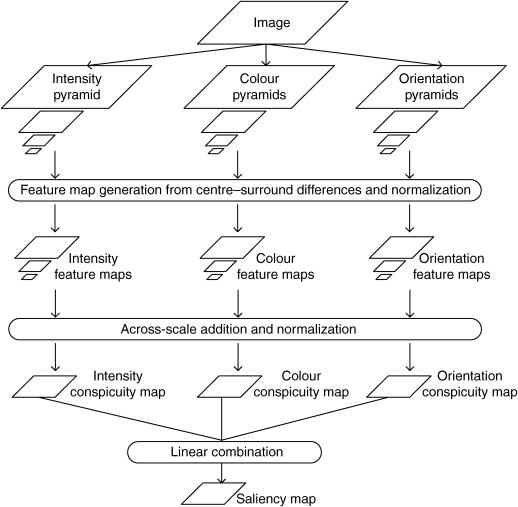
In Figure 3.1 the low-level features of an input still image for three channels (intensity, colour and orientation) are extracted and each channel is decomposed into a pyramid with nine scales. The centre–surround processing between different scales is performed to create several feature maps for each channel. Then fusing of across-scale and normalization for these channels produces three conspicuity maps. Finally, the three conspicuity maps are combined into a saliency map of the visual field. As mentioned above, the saliency map is the computational result of the attention model.
There are five characteristics of the core of this bottom-up visual attention model:
Get Selective Visual Attention: Computational Models and Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

