Synthesis of Arithmetic Circuits: FPGA, ASIC and Embedded Systems
by Jean-Pierre Deschamps, Gery J.A. Bioul, Gustavo D. Sutter
11.1 NATURAL NUMBERS
11.1.1 Basic Adder (Ripple-Carry Adder)
The structure of an n-digit ripple-carry adder is shown in Figure 11.1. The full adder (FA) cell calculates q(i + 1) and z(i) as a function of x(i), y(i), and q(i), according to the iteration body of Algorithm 4.1:

Figure 11.1 Basic adder.
![]()
Let CFA and TFA be the cost and the computation time of an FA cell. The cost and computation time of an n-digit basic adder are equal to
![]()
Examples 11.1
- In base 2 the FA equations (11.1) are

(∨: or function, ⊕ : xor function).
- In base 10 the FA equations are
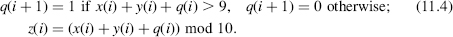
The decimal digits can be represented as 4-bit binary numbers (BCD—binary-coded decimal representation) so that a decimal full adder is a 9-input, 5-output binary circuit. It can be implemented using classical methods and tools of combinational logic synthesis. Another option is to decompose it further on. The following algorithm computes (11.4):
s:=x(i)+y(i)+q(i); if s>9 then z(i):=(s+6) mod 16; q(i+1):=1; else z(i):=s; q(i + 1):=0; ...