Installation
A planned secure installation of SQL Server is the vital first step in building a protected database server. These initial steps define much of the server's underlying security.
Step 1: Authentication
Setting the server on install to use integrated Windows authentication instead of native SQL Server authentication simplifies security administration and reduces the risks of attacks from password sniffing. The authentication mode can be set during the server's installation as shown in Figure 23-1.
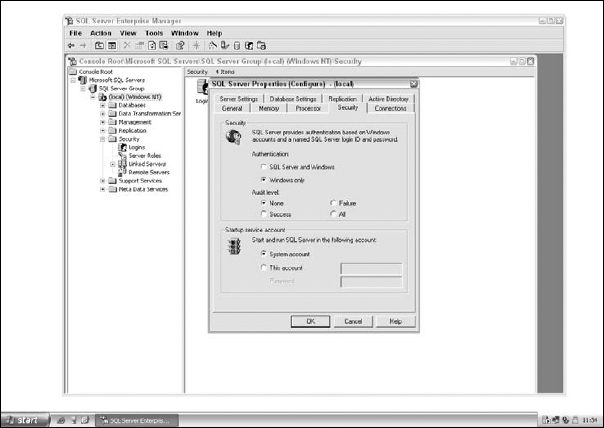
The authentication mode can also be changed later using the SQL Server Enterprise Manager, under the Security tab of the SQL Server's properties, which is shown in Figure 23-2.
The authentication mode can also be changed using the registry keys:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\MSQLServer\LoginMode HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\[Instance]\LoginMode
A value of 1 signifies Windows authentication; 2 denotes both native and Windows authentication.
Figure 23-1 Setting the authentication mode.
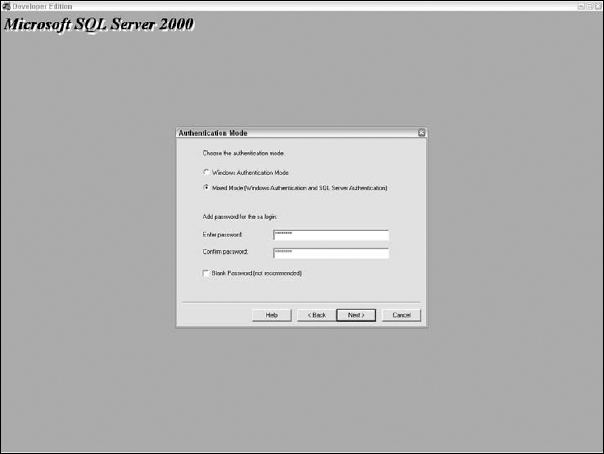
Figure 23-2 Changing the authentication mode.
In SQL Server 6.5, the Enterprise Manager stored the sa password in the registry in plaintext. Although SQL Server 7 and 2000 do obfuscate this information, it is the same method used to hide ODBC credentials ...
Get The Database Hacker's Handbook: Defending Database Servers now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

