3.3 STRUCTURE OF THE STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION
3.3.1 Equity versus Balanced Formats
Exhibit 3-1 illustrates the basic formats and basic forms of the statement of financial position.
Exhibit 3-1 Basic Formats and Basic Forms of the Statement of Financial Position
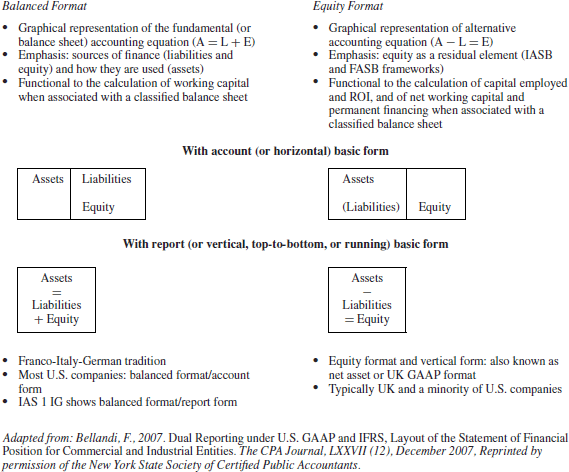
3.3.1.1 Basic Formats
Get The Handbook to IFRS Transition and to IFRS U.S. GAAP Dual Reporting now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

