Chapter 6. 3D Graphics
Unity has become increasingly well known for the visual quality of its rendering engine, and a huge part of that is due to the flexibility it offers artists. In this chapter, we’ll take a close look at materials, shaders, and lighting, and how you can build your own effects that suit the unique look of your own game.
Tip
We strongly recommend also reviewing the recipes in Chapter 5 for more complete coverage of graphics topics.
6.1 Creating a Simple Material
Problem
You want to customize the appearance of the surface of a 3D object by creating a material.
Solution
In this recipe, we’ll customize a simple shape, though the steps apply to most other meshes you’ll end up using in your game:
-
Create a new sphere by opening the GameObject menu and choosing 3D Object → Sphere.
-
Open the Assets menu and choose Create → Material. Name it whatever you like.
-
Select the new material, and configure its colors (Figure 6-1).
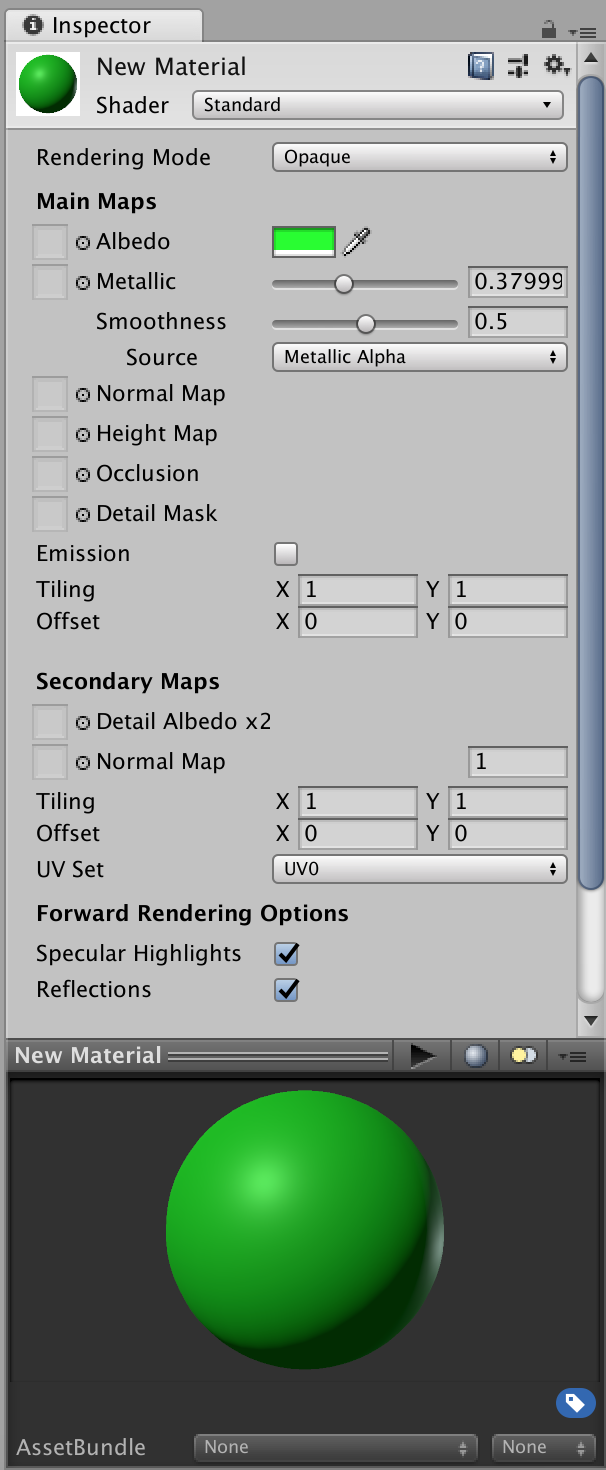
Figure 6-1. The Inspector for a material. This shows the configurable properties for the default Standard shader.
-
Drag and drop the material onto the sphere.
Discussion
Materials are essential to controlling the appearance of objects in your scene. Materials work by combining a shader, which is a program that computes the final color of each pixel that makes up an object, with properties, which are inputs delivered to the shader ...
Get Unity Game Development Cookbook now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

