CONTINGENT CLAIMS APPROACH: OPTION VALUATION METHOD
The last of the valuation approaches I will discuss are those that use option valuation methods. To see why option valuation concepts are relevant to the valuation of equity, consider a firm with a single $5 million face value, zero-coupon debt issue outstanding that matures in one year. Furthermore, assume that VF * is the value of the assets of the firm when the debt matures a year from now.
Figure 13.5 shows the payoffs to the debtholders and to the equityholders when the debt in this example matures. If the firm is worth more than $5 million, the debtholders will be paid off in full and the shareholders will get any residual value above the $5 million face value of the debt, F. If the value of the firm is below $5 million, the debtholders, at least in theory, get the firm. In other words, the shareholders have an option to default. The shareholders’ downside is limited to what they have already invested in the firm, and the debtholders receive the residual value of the firm if that option is exercised.
FIGURE 13.5 Option Characteristics of Debt and Equity Claims
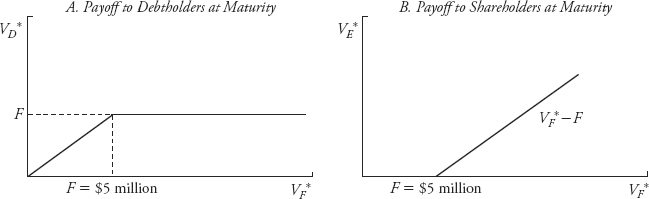
Another way of thinking about this idea is to realize that the shareholders essentially have a call option on the underlying assets of the firm. When the debt matures, the shareholders have the option to pay off the debt or walk away. If, on the one hand, the value ...
Get Valuation Techniques: Discounted Cash Flow, Earnings Quality, Measures of Value Added, and Real Options now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

