3.2 Overview of the State of the Art
Modern video transmission and storage systems are typically characterized by a wide range of access network technologies and end-user terminals. Varying numbers of users, each with their own time-varying data throughput requirements, adaptively share network resources, resulting in dynamic connection qualities. Users possess a variety of devices with different capabilities, ranging from cell phones with small screens and restricted processing power to high-end PCs with high-definition displays. Examples of applications include virtual collaboration system scenarios, as shown in Figure 3.2, where a large, high-powered terminal acts as the main control/command point and serves a group of co-located users. This may be the headquarters of an organization and consist of communication terminals, shared desk spaces, displays and various user-interaction devices for collaborating with remotely-located partners. The remotely-located users with small fixed terminals will act as local contacts and provide local information. Mobile units (distribution, surveying, marketing, patrolling, and so on) of the organization may use mobile terminals, such as mobile phones and PDAs, to collaborate with the headquarters.
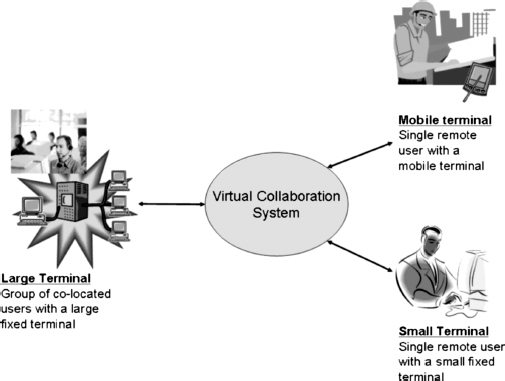
Figure 3.2 Virtual collaboration system diagram
In order to cope with the heterogeneity of networks/terminals and diverse user preferences, the current ...