5.3 Rate Control Architecture for Joint MVS Encoding and Transcoding
5.3.1 Problem Definition and Objectives
Compliant video encoding, whatever the video coding standard, requires adequate control of the video encoder, meeting relevant constraints of the encoding framework, notably: bit rate, delay, complexity, and quality.
Several relevant applications may require the transmission of multiple video sequences or video scenes composed of multiple VOs, through a common constant bit rate (CBR) channel, for example broadcasting, video monitoring and surveillance, telemedicine, and video conferencing.
In this context, two different rate control scenarios have been identified:
- Joint MVS encoding scenario: In this scenario multiple video sequences (or a video scene composed of multiple VOs) are jointly encoded, dynamically sharing along time the available channel bit rate and buffer constraints.
Figure 5.1(a) illustrates the joint encoding of multiple frame-based video sequences, encoding compliantly with the H.264/AVC video coding standard. In this case the rate controller is responsible for controlling multiple H.264/AVC encoders deciding the optimal (in an RD-complexity sense) spatio-temporal resolutions, bit allocations, and corresponding set of coding parameters for each input raw video sequence.
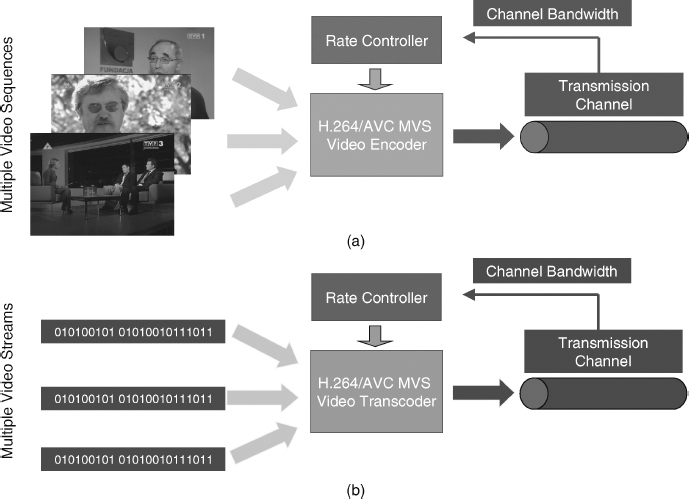
Figure 5.1 Rate control scenarios: (a) joint multiple video sequence encoding; (b) joint ...
Get Visual Media Coding and Transmission now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

