7.5 MATRIX-MATRIX MULTIPLICATION AND 2D SYSTOLIC ARRAY DESIGN
In this section, systolic arrays are designed for matrix-matrix multiplication [4]. The DG for this problem corresponds to a three-dimensional (3D) space representation. Linear projection is used to design 2D systolic arrays for matrix-matrix multiplication.
Given 2 matrices A and B, we can denote their product as C = AB, where A, B, and C are n × n matrices. For n = 2, we have
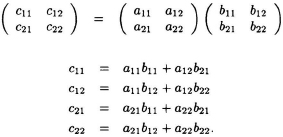
These equations can be represented in a space representation as shown in Fig. 7.17.
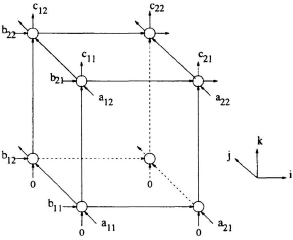
Fig. 7.17 Systolic array architecture of the matrix product computation.
From the space diagram, we can write the iteration in standard output RIA form as follows:
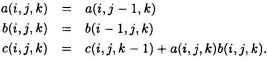
The corresponding RDG is shown in Fig. 7.18. Now, applying the scheduling inequality for each edge in the RDG sTe + γy − γx ≥ Tx and assuming
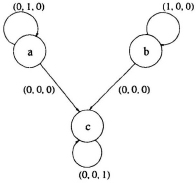
Fig. 7.18 Reduce dependence graph of the matrix product computation.
Tmult−add = 1 and Tcom = 0, we have,
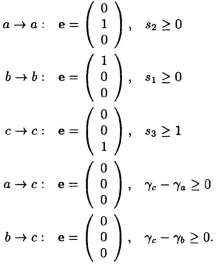
For linear scheduling, γa = γb = γc = 0. Consider ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

