9.2 PARALLEL FIR FILTERS
This section considers the implementation of parallel FIR filters using algorithmic strength reduction transformation.
9.2.1 Formulation of Parallel FIR Filtering Using Polyphase Decomposition
This section addresses the formulation of parallel FIR filters using polyphase decomposition, a technique used in multirate signal processing [1].
An N-tap FIR filter can be expressed in time domain as
![]()
where {x(n)} is an infinite length input sequence and the sequence {h(n)} contains FIR filter coefficients of length N, or in z-domain as
![]()
The input sequence {x(0), x(1), x(2), x(3), ···} can be decomposed into even- numbered part and odd-number part as follows:
![]()
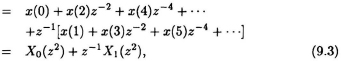
where X0(z2) and X1 (z2) are the z-transforms of x(2k) and x(2k + 1) (for 0 ≤ k < ∞), respectively. In (9.3), X(z) is decomposed into two polyphases. Similarly, the length-N filter coefficients H(Z) can be decomposed as
![]()
where H0(z2) and H1(z2) are of length N/2 and are referred to as even subfilter and odd subfilter, ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

