2.1 PSTN AND VoIP
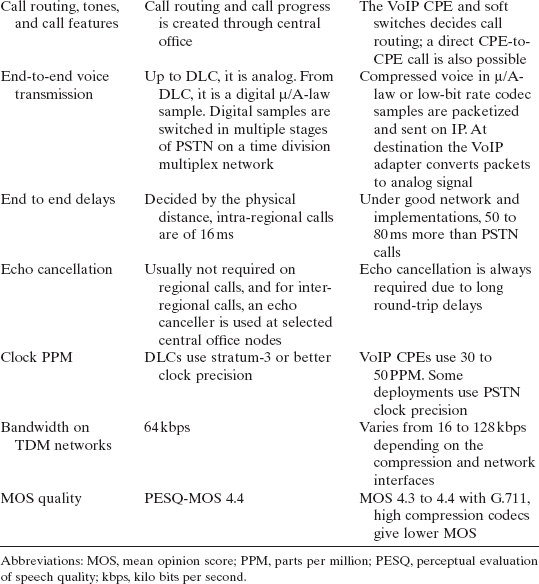
In this section, public switched telephone network (PSTN) and VoIP mapping and different VoIP basic call combinations are given. PSTN-based voice calls and infrastructure have been familiar to users for several decades. Functionally, a user will be using PSTN and VoIP in a similar way. However, several differences between PSTN and VoIP exist in actual implementation and end-to-end transmission. In Table 2.1, some key aspects and functional differences are given. A functional representation of a PSTN-based voice call is given in Fig. 2.1(a). VoIP calls can be mapped very closely to PSTN on an IP network as shown in Fig. 2.1(b). VoIP customer premises equipment (CPE) resides close to the end user of the VoIP service.
Table 2.1. PSTN and VoIP Comparison Overview

2.1.1 CPE and Naming Clarifications of VoIP Systems in this Book
In this book, CPE, VoIP adapter, and VoIP gateway names are used frequently and interchangeably. A VoIP CPE name is generic in that it accommodates several end-user boxes such as VoIP adapters, integrated access devices (IADs), residential gateways (RGs), home gateways (HGs), terminal adapters (same as VoIP adapters), wireless fidelity (WiFi) IP phones, IP phones, VoIP soft phones on computers, and any new systems that are positioned directly ...
Get VoIP Voice and Fax Signal Processing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

