4.3 COMFORT NOISE PAYLOAD FORMAT
As explained in the previous section, two popular types of VAD/CNG schemes are included in G.711. The noise power levels in both VAD/CNG methods are expressed in −dBov to interoperate with each other. The unit “dBov” is the dB level relative to the overload of the system. It is not a Volts reference for dBV. For example, in the case of μ-law-based coding, the maximum sine wave signal power without distortion is 3.17 dBm with amplitude ±8159. Square wave power is 3 dB more than sine wave power. The maximum possible power of signal from a square wave with an amplitude of ±8159 is 0 dBov as reference, which corresponds to a 6.17-dBm power level in the μ-law system. Hence, 0 dBov = 6.17 dBm is used in μ-law system. Sine and square wave power levels and signal amplitudes are shown in Fig. 4.1(c). Representation relative to the overload point of a system is particularly useful for digital implementations, because one does not need to know the relative calibration of the analog circuitry.
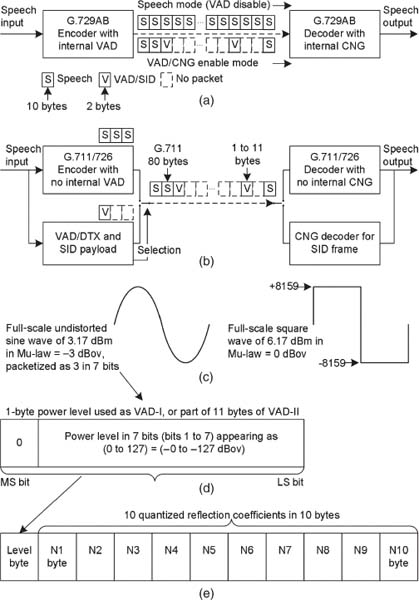
Figure 4.1. VAD/CNG representations. (a) VAD/CNG operation with G.729AB built-in VAD/CNG. (b) VAD/CNG with external VAD/CNG. (c) Power-level mapping with sine and square wave. (d) 1-byte power payload. (e) 11 bytes of payload.
Noise power levels in VAD are comparable from −40 to −60 dBm. The noise power is represented as −dBov with input power ranging from 0 to −127 dBov. ...
Get VoIP Voice and Fax Signal Processing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

