15.5 FAX PASS-THROUGH
The fax pass-through call flow is shown in Fig. 15.4. In the absence of T.38 and data pump support, or if interoperation of T.38 and a data pump is an issue, a fax is transmitted in pass-through mode using the G.711 codec [URL (Cisco-fax3)]. Fax pass-through is the simplest technique for sending a fax over IP networks. In all VoIP deployments, G.711 is supported. Once a VoIP G.711 call is established, the fax in pass-through mode works similarly to a PSTN-based fax call. In fax pass-through mode, gateways do not distinguish a fax call from a voice call. When an initial voice call is established with low-bit-rate compression codecs like G.729AB/G.723.1A, on detection of CED or ANS or/ANSam or V.21 preamble flag by the gateway, the codec will be switched to G.711 (PCMU or PCMA) with no VAD and no echo cancellation for the duration of the fax session. If an initial voice call is established with G.711 or G.726–32 kbps, then on detection of the ANS family of tones, the gateway modifies the other modules like EC and VAD for the duration of the fax session. In this scenario, a codec will not be modified. The VoIP gateway in pass-through mode performs the following functional SIP call events to establish a fax pass-through call:
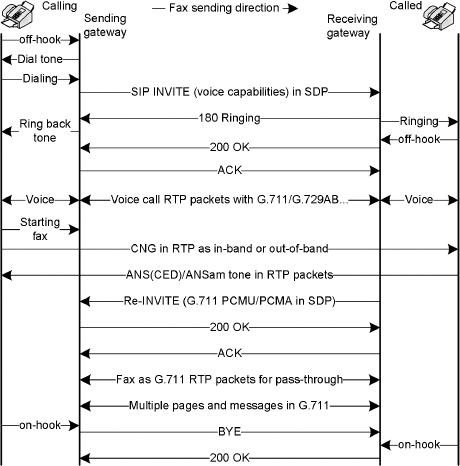
Figure 15.4. Fax pass-through call flow.
- The initial call is established like a voice call with a dial plan.
- The receiving or terminating ...
Get VoIP Voice and Fax Signal Processing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

