Flash Interface Basics
To better understand the way Flash handles multimedia content, it is useful to be generally acquainted with the Flash authoring environment. Figure 35-1 shows the core features of the Flash interface as seen on Windows XP.
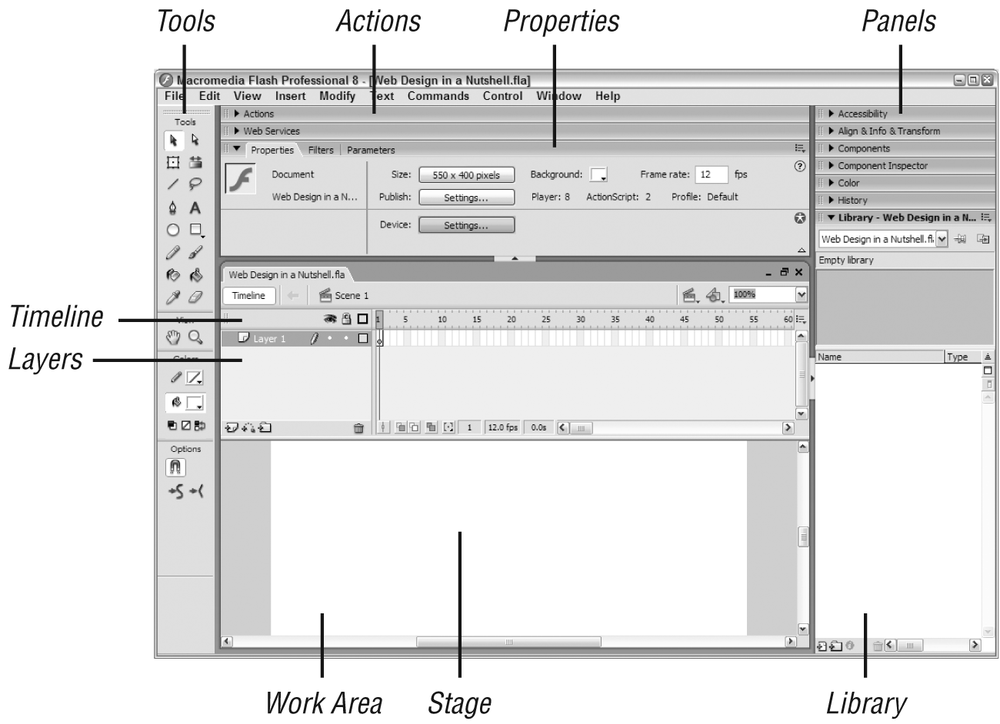
Figure 35-1. The Flash interface
- Tools
The Toolbox contains all the tools for drawing, painting, selecting, viewing, and modifying artwork.
- Stage
The Stage is the area where you compose and preview the movie.
- Layers
The elements on a Timeline may be stored on separate layers (similar to layers in image editing tools). Layers in Flash control the arrangement of objects from background to foreground, support masking, enable motion and shape tweening, and contain guide elements, frame labels, and actions.
- Timeline
The Timeline is where you control the timing of the animation and assemble the elements from separate layers.
- Frames
Like film, Flash movies divide lengths of time into individual frames. A keyframe is a frame in which you define a change in the animation. Static frames reflect no change and merely repeat the content of the prior frame. Animation effects are added by changing content over a series of frames.
- Library
The Library is where you store all imported items (such as images and audio), native symbols (Flash objects that you want to use repeatedly in the same movie, such as a button), and components (Flash objects that you can ...