MapScript Examples
MapServer map files are still a key component to writing a MapScript-based application. If you have a map file ready to use, you can start accessing and manipulating it right away. However, a powerful feature of MapScript is the ability to create maps on the fly without having a map file. In this case, you can build your map from scratch.
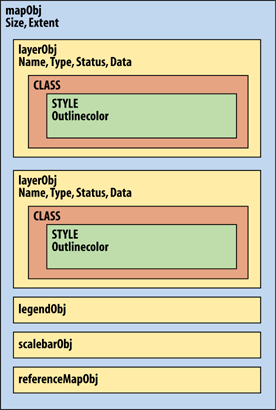
Figure 14-1. The MapScript API's hierarchical object structure
In the first two examples, a simple map file is used, as shown in Example 14-1. In the third example, a custom map file is created using MapScript. To keep the example short and simple, I've removed optional components like the scale bar, legend, and reference map.
Example 14-1. A simple map file used for the examples in this chapter
MAP
SIZE 600 300
EXTENT -180 -90 180 90
IMAGECOLOR 180 180 250
IMAGETYPE PNG
UNITS DD
WEB
IMAGEPATH "/srv/www/htdocs/tmp/"
IMAGEURL "/tmp/"
END
LAYER
NAME countries
TYPE POLYGON
STATUS DEFAULT
DATA countries_simpl
CLASS
NAME 'Countries'
OUTLINECOLOR 100 100 100
COLOR 200 200 200
END
END
ENDTip
You can download the country boundary data in shapefile format from http://ftp.intevation.de/freegis/worlddata/freegis_worlddata-0.1_simpl.tar.gz.
This compressed file contains a shapefile called countries_simpl. The map file example assumes that the countries_simpl.* files are in the same folder as the map file. This dataset is used elsewhere in this book. ...