Defragmentation
Fragmentation is a term used to describe the degree of contiguousness in the clusters allocated to a file. When a filesystem is first created, there is plenty of space available on that partition. As users create new files or extend the size of existing ones, the filesystem is able to allocate contiguous clusters from its free list. As the filesystem fills up, it cannot satisfy requests for additional capacity using contiguous clusters and starts to use available clusters from any location on the surface of the disk. Figure 9-12 shows the allocation of two files on a partition. File A consists of 7 clusters, most of which are contiguous; File B consists of only four clusters, none of which are contiguous. When a user tries to read the entire contents of File A, the disk can retrieve the contents of that file very efficiently because they are located close to one another on the disk. If the user generates a similar read request against File B, the disk needs to seek around the surface of the disk in order to locate all the fragments that comprise the file, thus degrading the performance of the disk subsystem.
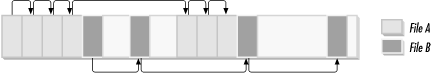
Figure 9-12. File B is more fragmented than File A
There is a rumor in the industry that partitions formatted with the NTFS filesystem do not get fragmented. Although NTFS uses more advanced algorithms in allocating clusters to files, it is not immune to fragmentation. ...
Get Windows 2000 Performance Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

