9.2 TASK ASSIGNMENT IN MULTIROBOT SYSTEMS
Multirobot systems (MRS) are well studied in literature and several survey papers, taxonomies, and book chapters exist on the subject (e.g., Dudek et al., 2002; Farinelli et al., 2004; Parker et al., 2008). The focal point of the majority of MRS-related papers is on general communication, coordination, and cooperation. Networked robotics is an extension of MRS where communication between entities is fundamental to both cooperation and coordination, and hence the central role of the network (Bekey and Yuh, 2008; Kumar et al., 2008). Applications of networked robots include coupling to perform locomotion and manipulation tasks, and coordinating to perform exploration, mapping, search and reconnaissance tasks, or gaming (e.g., robot soccer). They can also perform independent tasks that need to be coordinated (e.g., hole drilling or welding).
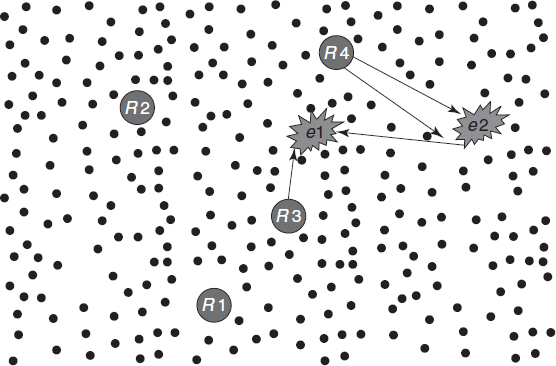
Figure 9.2 Monitored area with two concurrent events and two possible assignments.
We also use the term wireless sensor and robot network (WSRN). It addresses the special case when robots are used as mobile actors within sensor networks. An illustration is given in Figure 9.2, showing sensors, four robots, and two events. Wireless sensor and robot networks are characterized by real-time response constraints and sensor-sensor, sensor-robot, and robot-robot coordination. Sensors-robot coordination provides ...
Get Wireless Sensor and Actuator Networks: Algorithms and Protocols for Scalable Coordination and Data Communication now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

