7
Broadband Wireless Access: WLAN, Wi-Fi and WiMAX
7.1 Wireless Technology Differentiation
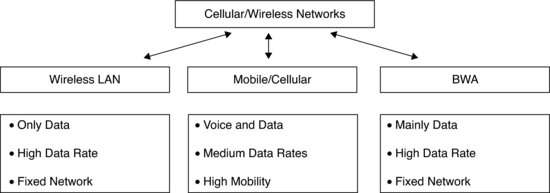
The wireless networks, under three categories, are shown in Figure 7.1: Mobile networks, Wireless LAN and Broadband Wireless networks. While cellular networks are about both voice and data, wireless LAN networks are only data. BWA networks are mainly data. Both WLAN and BWA fall predominantly under the fixed category. In this chapter we will take a closer look at the WLAN and BWA (Wi-Fi and WiMAX) networks.
Figure 7.1 Wireless technology differentiation.
7.1.1 Broadband Wireless Access
Broadband Wireless Access or BWA is a radio access technology that is used to deliver broadband services to the users’ premises. Broadband refers to having an instantaneous bandwidth greater than 1 MHz while supporting data rates of/more than 1.5 Mbps (802.16-2004 standard). The services are delivered via radio and user-to-user connections are less. If there is a user-to-user connection, it is made via the core network. The available bandwidth is shared between the users that are covered under one coverage area. As the user requirements are many, BWA networks deliver both voice and other kinds of data services. Under deregulated markets, for operators without existing wired infrastructure, wireless broadband networks offer an exciting opportunity as they are quick and easy to deploy resulting in less time ...

