Chapter 16. Maps
The Map interface is the last of
the major Collections Framework interfaces, and the only one that does not inherit
from Collection. It defines the
operations that are supported by a set of key-to-value associations in which
the keys are unique. These operations are shown in Figure 16-1
and fall into the following four groups, broadly parallel to the four
operation groups of Collection—adding
elements, removing elements, querying collection contents, and providing
different views of the contents of a collection.
Adding Associations
V put(K key, V value) // add or replace a key-value association
// return the old value (may be null) if the
// key was present; otherwise returns null
void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m)
// add each of the key-value associations in
// the supplied map into the receiver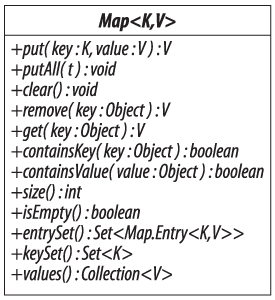
The operations in this group are optional; calling them on an
unmodifiable map will result in an UnsupportedOperationException.
Removing Associations
void clear() // remove all associations from this map
V remove(Object key) // remove the association, if any, with the
// given key; returns the value with which it
// was associated, or nullThe signature of Map.remove is like
that of the Collection.remove (see Using the Methods of Collection) in that it takes a parameter
of type Object rather than the generic type. We discussed alternatives to this design ...
Get Java Generics and Collections now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

