3.4 Protocols
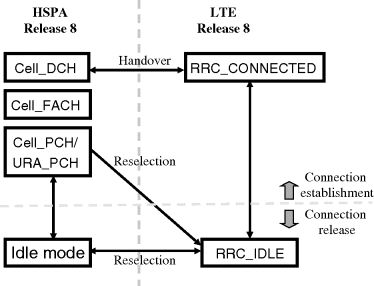
As visible in Figure 3.11, all the LTE user plane and control plane radio protocols terminate in the eNodeB. On the control plane side the Radio Resource Control (RRC) protocol provides the UE the RRC control messages which included configuring the connection parameters, control of the mobility measurement and procedures, measurement reports from the UE to the eNodeB, handover commands from the network to the UE and so on. Similar to the HSPA the same ASN.1 encoding is used with LTE, allowing extensions with newer 3GPP Releases to be implemented in a backwards compatible way. The key difference to HSPA is the definition of only two RRC states, as shown in Figure 3.12.
Figure 3.12 LTE and HSPA Release 8 RRC states.
The Medium Access Control (MAC) is part of the layer 2 protocols with the key functional split shown in Figure 3.13 showing the data flow radio bearers all the way to the physical layer. The MAC has the following key functionalities:
- Physical layer retransmission handling;
- Scheduling;
- Priority handling;
- Multiplexing of different logical channels to a single transport channel.
As part of the MAC layer operation, the MAC header can contain control information also, such as in the downlink direction the uplink timing advance is part of the MAC layer signalling while in the uplink direction the buffer status reports can indicate how much and what kind of data ...
Get LTE Advanced: 3GPP Solution for IMT-Advanced now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

