14.5 RADIX-2 HYBRID REDUNDANT MULTIPLICATION ARCHITECTURES
This section considers design of bit-serial radix-2 hybrid redundant number based on-line multiplication. These redundant multipliers process the msd of the input data first and generate the msd of the result first. On-line arithmetic leads to low−latency architectures and is useful for operations such as division and square root which are inherently msd-first operations.
Consider multiplication of 2 numbers, A = a3.a2a1a0 and B = b3.b2b1b0, using the 2 multiplication dependence graphs (DGs) shown in Fig. 14.11 and Fig. 14.12. The basic processing element (the black solid circle in the DGs) carries out an add operation defined by the following equation :
![]()
where the dashed lines represent carry and the solid lines represent sum. The elliptic circles on the last row are dummy operations used only to group the bits together to form the product digits. In the DG of Fig. 14.11, the carry moves vertically down whereas it moves diagonally in the DG of Fig. 14.12 [19].
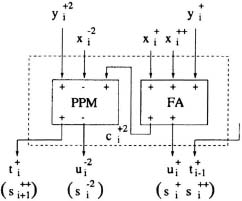
Fig. 14.9 Minimally Redundant HYbrid radix-4 Adder cell (mrHY4A).
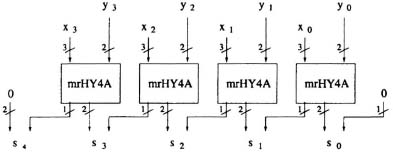
Fig. 14.10 Four-digit mrHY4A.
Using systolic design methodology (see Chapter 7), and the following ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

