11.5 VoIP VOICE PACKETS ON A CABLE INTERFACE
As shown in Fig. 11.2(c), VoIP CPE is used with a cable interface. An Ethernet interface joins with a cable modem in residential applications. Both VoIP CPE and a cable modem can be on the same box. The data-over-cable system has two streams: cable modem (CM) to CM terminal system (CMTS) as the upstream direction, and CMTS to CM through the cable network as the downstream direction (traffic toward the CPE). In the data-over-cable system, the services used for VoIP are Unsolicited Grant Service or Unsolicited Grant Service with activity detection to support real-time service flows that generate fixed-size data packets (like voice) on a periodic basis as given in the DOCSIS 1.1 document [DOCSIS 1.1 (2005)]. Figure 11.4(c) shows a normal RTP packet carried on a downstream channel. It is similar to an upstream channel packet except for the physical layer overhead.
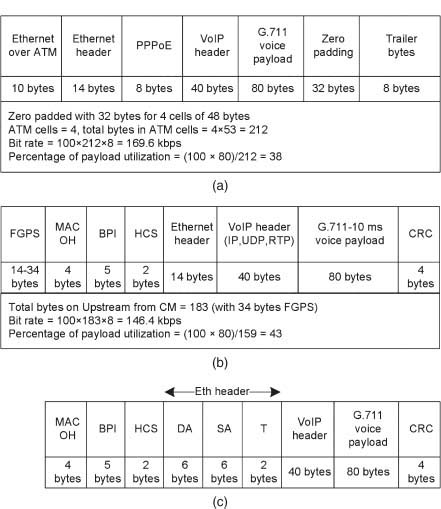
Figure 11.4. Packet format examples with G.711-10 ms on DSL and cable interfaces. (a) DSL with PPPoE. (b) Cable upstream is with 34 bytes of FGPS calculation. (c) Cable downstream.
Figure 11.4(b) shows a normal RTP packet carried on an upstream channel. In this section, an overview with example headers is given. More details are available in the DOCSIS 1.1 document. The header level description of upstream and downstream packets is given here:
FGPS: Physical layer overhead F-FEC, ...
Get VoIP Voice and Fax Signal Processing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

