13.4 BIT-SERIAL MULTIPLIERS
This section addresses the derivation of Lyon’s bit-serial multiplier [14] using Horner’s rule. Several other bit-serial multipliers are then derived using systolic mapping techniques.
13.4.1 Design of Lyon’s Bit-Serial Multipliers Using Horner’s Rule
The multiplication rule in (13.5) can be used to derive bit-serial multipliers. The architecture for a 4 × 4-bit bit-serial multiplication is shown in Fig. 13.14(a), where the ![]() is a bit-serial zero-latency scaling operator and its functionality is illustrated in Fig. 13.14(b). For a bit-serial zero-latency system, the first output bit needs to be generated in the same clock cycle as the first input bit entering the system. For the scaling operator, the first output bit a1 should be generated at the same time instance when the first input a0 enters the operator. Since input a1 has not entered the system yet, the scaling operator is a noncausal or advance operation, and cannot be implemented in hardware.
is a bit-serial zero-latency scaling operator and its functionality is illustrated in Fig. 13.14(b). For a bit-serial zero-latency system, the first output bit needs to be generated in the same clock cycle as the first input bit entering the system. For the scaling operator, the first output bit a1 should be generated at the same time instance when the first input a0 enters the operator. Since input a1 has not entered the system yet, the scaling operator is a noncausal or advance operation, and cannot be implemented in hardware.
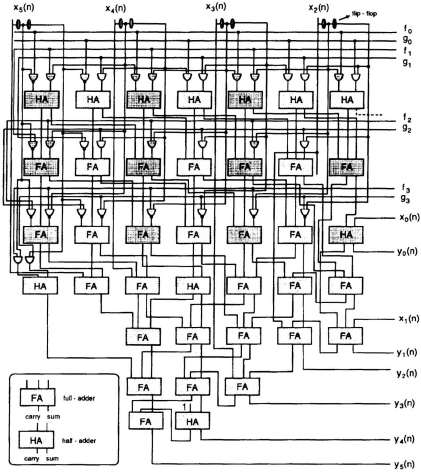
Fig. 13.11 Architecture for the multiplication chart shown in Fig. 13.10.
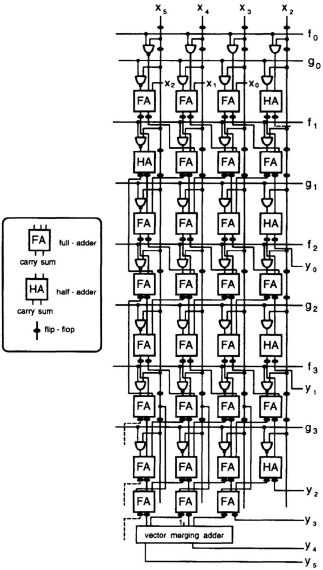
Fig. 13 12 Bit-plane architecture for the multiplication chart shown in Fig. 13.10.
Fig. 13.13 Multiplication chart for ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

