11
Scrolling
In this chapter:
- Scrollbar
- Scrolling An Image
- The Adjustable Interface
- ScrollPane
This chapter describes how Java deals with scrolling. AWT provides two means for scrolling. The first is the fairly primitive Scrollbar object. It really provides only the means to read a value from a slider setting. Anything else is your responsibility: if you want to display the value of the setting (for example, if you're using the scrollbar as a volume control) or want to change the display (if you're using scrollbars to control an area that's too large to display), you have to do it yourself. The Scrollbar reports scrolling actions through the standard event mechanisms; it is up to the programmer to handle those events and perform the scrolling.
Unlike other components, which generate an ACTION_EVENT when something exciting happens, the Scrollbar generates five events: SCROLL_LINE_UP, SCROLL_LINE_DOWN, SCROLL_PAGE_UP, SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN, and SCROLL_ABSOLUTE. In Java 1.0, none of these events trigger a default event handler like the action() method. To work with them, you must override the handleEvent() method. With Java 1.1, you handle scrolling events by registering an AdjustmentListener with the Scrollbar.addAdjustmentListener() method; when adjustment events occur, the listener's adjustmentValueChanged() method is called.
Release 1.1 of AWT also includes a ScrollPane container object; it is a response to one of the limitations of AWT 1.0. A ScrollPane is like a Panel, but it has scrollbars and scrolling built in. In this sense, it's like TextArea, which contains its own scrollbars. You could use a ScrollPane to implement a drawing pad that could cover an arbitrarily large area. This saves you the burden of implementing scrolling yourself: generating scrollbars, handling their events, and figuring out how to redisplay the screen accordingly.
Both Scrollbar and ScrollPane take advantage of the Adjustable interface. Adjustable defines the common scrolling activities of the two classes. The Scrollbar class implements Adjustable; a ScrollPane has two methods that return an Adjustable object, one for each scrollbar. Currently, you can use the ScrollPane's “adjustables” to find out the scrollbar settings in each direction. You can't change the settings or register AdjustmentListeners; the appropriate methods exist, but they don't do anything. It's not clear whether this is appropriate behavior or a bug (remember, an interface only lists methods that must be present but doesn't require them to do anything); it may change in a later release.
11.1 Scrollbar
Scrollbars come in two flavors: horizontal and vertical. Although there are several methods for setting the page size, scrollbar range (minimum and maximum values), and so on, basically all you can do is get and set the scrollbar's value. Scrollbars don't contain any area to display their value, though if you want one, you could easily attach a label.
To work with a Scrollbar, you need to understand the pieces from which it is built. Figure 11-1 identifies each of the pieces. At both ends are arrows, which are used to change the Scrollbar value the default amount (one unit) in the direction selected. The paging areas are used to change the Scrollbar value one page (ten units by default) at a time in the direction selected. The slider can be moved to set the scrollbar to an arbitrary value within the available range.
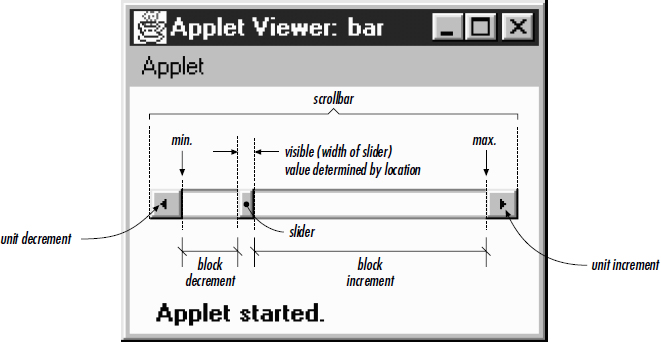
Figure 11–1: Scrollbar elements
11.1.1 Scrollbar Methods
Constants
There are two direction specifiers for Scrollbar. The direction tells the Scrollbar which way to orient itself. They are used in the constructors, as a parameter to setOrientation(), and as the return value for the getOrientation() method.
public final static int HORIZONTAL
HORIZONTAL is the constant for horizontal orientation.
public final static int VERTICAL
VERTICAL is the constant for vertical orientation.
Constructors
public Scrollbar (int orientation, int value, int visible, int minimum, int maximum)
The Scrollbar constructor creates a Scrollbar with a direction of orientation and initial value of value. visible is the size of the slider. minimum and maximum are the range of values that the Scrollbar can be. If orientation is not HORIZONTAL or VERTICAL, the constructor throws the run-time exception IllegalArgumentException. If maximum is below the value of minimum, the scrollbar's minimum and maximum values are both set to minimum. If value is outside the range of the scrollbar, it is set to the limit it exceeded. The default line scrolling amount is one. The default paging amount is ten.
If you are using the scrollbar to control a visual object, visible should be set to the amount of a displayed object that is on the screen at one time, relative to the entire size of the object (i.e., relative to the scrollbar's range: maximum-minimum). Some platforms ignore this parameter and set the scrollbar to a fixed size.
public Scrollbar (int orientation)
This constructor for Scrollbar creates a Scrollbar with the direction of orientation. In Java 1.0, the initial settings for value, visible, minimum, and maximum are 0. In Java 1.1, the default value for visible is 10, and the default for maximum is 100; the other values default to 0. If orientation is not HORIZONTAL or VERTICAL, the constructor throws the run-time exception IllegalArgumentException. This constructor is helpful if you want to reserve space for the Scrollbar on the screen, to be configured later. You would then use the setValues() method to configure the scrollbar.
This constructor creates a VERTICAL Scrollbar. In Java 1.0, the initial settings for value, visible, minimum, and maximum are 0. In Java 1.1, the default value for visible is 10, and the default for maximum is 100; the other values default to 0. You would then use the setValues() method to configure the scrollbar.
Figure 11-2 shows both vertical and horizontal scrollbars. It also demonstrates a problem you'll run into if you're not careful. If not constrained by the LayoutManager, scrollbars can get very fat. The result is rarely pleasing. The solution is to place scrollbars in layout managers that restrict width for vertical scrollbars or height for horizontal ones. The side regions (i.e., everything except the center) of a border layout are ideal. In the long term, the solution will be scrollbars that give you their maximum size and layout managers that observe the maximum size.
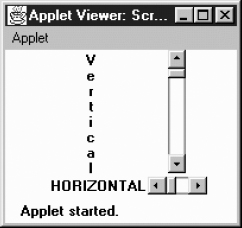
Figure 11–2: Vertical and horizontal scrollbars
Adjustable Methods
public int getOrientation ()
The getOrientation() method returns the current orientation of the scrollbar: either Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL or Scrollbar.VERTICAL.
public synchronized void setOrientation (int orientation) ![]()
The setOrientation() method changes the orientation of the scrollbar to orientation, which must be either Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL or Scrollbar.VERTICAL. If orientation is not HORIZONTAL or VERTICAL, this method throws the run-time exception IllegalArgumentException. It was not possible to change the orientation of a scrollbar prior to Java 1.1.
public int getVisibleAmount () ![]()
public int getVisible () ![]()
The getVisibleAmount() method gets the visible setting of the Scrollbar. If the scrollbar's Container is resized, the visible setting is not automatically changed. getVisible() is the Java 1.0 name for this method.
public synchronized void setVisibleAmount (int amount) ![]()
The setVisibleAmount() method changes the current visible setting of the Scrollbar to amount.
public int getValue ()
The getValue() method is probably the most frequently called method of Scrollbar. It returns the current value of the scrollbar queried.
public synchronized void setValue (int value)
The setValue() method changes the value of the scrollbar to value. If value exceeds a scrollbar limit, the scrollbar's new value is set to that limit. In Java 1.1, this method is synchronized; it was not in earlier versions.
public int getMinimum ()
The getMinimum() method returns the current minimum setting for the scrollbar.
public synchronized void setMinimum (int minimum) ![]()
The setMinimum() method changes the Scrollbar's minimum value to minimum. The current setting for the Scrollbar may change to minimum if minimum increases above getValue().
public int getMaximum ()
The getMaximum() method returns the current maximum setting for the scrollbar.
public synchronized void setMaximum (int maximum) ![]()
The setMaximum() method changes the maximum value of the Scrollbar to maximum. The current setting for the Scrollbar may change to maximum if maximum decreases below getValue().
public synchronized void setValues (int value, int visible, int minimum, int maximum)
The setValues() method changes the value, visible, minimum, and maximum settings all at once. In Java 1.0.2, separate methods do not exist for changing visible, minimum, or maximum. The scrollbar's value is set to value, visible to visible, minimum to minimum, and maximum to maximum. If maximum is below the value of minimum, it is set to minimum. If value is outside the range of the scrollbar, it is set to the limit it exceeded. In Java 1.1, this method is synchronized; it was not in earlier versions.
public int getUnitIncrement () ![]()
public int getLineIncrement () ![]()
The getUnitIncrement() method returns the current line increment. This is the amount the scrollbar will scroll if the user clicks on one of the scrollbar's arrows.
getLineIncrement() is the Java 1.0 name for this method.
public void setUnitIncrement (int amount) ![]()
public void setLineIncrement (int amount) ![]()
The setUnitIncrement() method changes the line increment amount to amount.
setLineIncrement() is the Java 1.0 name for this method.
Changing the line increment amount was not possible in Java 1.0.2. This method acted like it returned successfully, and getLineIncrement() returned the new value, but the Scrollbar changed its value by only one (the default) when you clicked on one of the arrows. However, you could work around this defect by explicitly handling the SCROLL_LINE_UP and SCROLL_LINE_DOWN events: get the correct line increment, adjust the display appropriately, and then set call setValue() to correct the scrollbar's value. This workaround is not needed in Java 1.1.
public int getBlockIncrement () ![]()
public int getPageIncrement () ![]()
The getBlockIncrement() method returns the current paging increment. This is the amount the scrollbar will scroll if the user clicks between the slider and one of the scrollbar's arrows.
getPageIncrement() is the Java 1.0 name for this method.
public void setBlockIncrement (int amount) ![]()
public void setPageIncrement (int amount) ![]()
The setBlockIncrement() method changes the paging increment amount to amount.
setPageIncrement() is the Java 1.0 name for this method.
Changing the paging increment amount was not possible in Java 1.0.2. This method acts like it returns successfully, and getPageIncrement() returns the new value, but the Scrollbar changes its value only by 10 (the default) when you click on one of the paging areas. However, you can work around this defect by explicitly handling the SCROLL_PAGE_UP and SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN events: get the correct page increment, adjust the display appropriately, and then set call setValue() to correct the scrollbar's value. This workaround is not necessary in Java 1.1.
Miscellaneous methods
public synchronized void addNotify ()
The addNotify() method creates the Scrollbar's peer. If you override this method, call super.addNotify() first. You will then be able to do everything you need with the information about the newly created peer.
protected String paramString ()
Scrollbar doesn't have its own toString() method; when you call the toString() method of a Scrollbar, you are actually calling the method Component.toString(). This in turn calls paramString(), which builds the string to display. For a Scrollbar, paramString() puts the scrollbar's value, visibility, minimum, maximum, and direction into the string. In Java 1.0, there is a minor bug in the output. Instead of displaying the scrollbar's visible setting (an integer), paramString() displays the component's visible setting (a boolean). (This is corrected in Java 1.1.) The following String is the result of calling toString() for a horizontal Scrollbar that hasn't been configured yet:
java.awt.Scrollbar[0,0,0x0,invalid,val=0,vis=true,min=0,max=0,horz]
11.1.2 Scrollbar Events
With the 1.0 event model, scrollbars generate five kinds of events in response to user interaction: SCROLL_LINE_UP, SCROLL_LINE_DOWN, SCROLL_PAGE_UP, SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN, and SCROLL_ABSOLUTE. The event that occurs depends on what the user did, as shown in Table 11-1; the event type is specified in the id field of the Event object passed to handleEvent(). However, as a programmer, you often do not care which of these five events happened. You care only about the scrollbar's new value, which is always passed as the arg field of the Event object.
| Event Type (Event.id) | Event Meaning |
| SCROLL_ABSOLUTE | User drags slider. |
| SCROLL_LINE_DOWN | User presses down arrow. |
| SCROLL_LINE_UP | User presses up arrow. |
| SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN | User selects down paging area. |
| SCROLL_PAGE_UP | User selects up paging area. |
Because scrollbar events do not trigger any default event handlers (like action()), it is necessary to override the handleEvent() method to deal with them. Unless your version of handleEvent() deals with all conceivable events, you must ensure that the original handleEvent() method is called. The simplest way is to have the return statement call super.handleEvent().
Most handleEvent() methods first identify the type of event that occurred. The following two code blocks demonstrate different ways of checking for the Scrollbar events.
if ((e.id == Event.SCROLL_LINE_UP) || (e.id == Event.SCROLL_LINE_DOWN) || (e.id == Event.SCROLL_PAGE_UP) || (e.id == Event.SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN) || (e.id == Event.SCROLL_ABSOLUTE)) { // Then determine which Scrollbar was selected and act upon it }
Or more simply:
if (e.target instanceof Scrollbar) {
// Then determine which Scrollbar was selected and act upon it.
}
Although the second code block is simpler, the first is the better choice because it is more precise. For example, what would happen if mouse events are passed to scrollbars? Different Java platforms differ most in the types of events passed to different objects; Netscape Navigator 3.0 for Windows 95 sends MOUSE_ENTER, MOUSE_EXIT, and MOUSE_MOVE events to the Scrollbar.* The second code block executes for all the mouse events—in fact, any event coming from a Scrollbar. Therefore, it executes much more frequently (there can be many MOUSE_MOVE events), leading to poor interactive performance.
Another platform-specific issue is the way the system generates SCROLL_ABSOLUTE events. Some platforms generate many events while the user drags the scrollbar. Others don't generate the event until the user stops dragging the scrollbar. Some implementations wait until the user stops dragging the scrollbar and then generate a flood of SCROLL_ABSOLUTE events for you to handle. In theory, it does not matter which is happening, as long as your event-processing code is tight. If your event-processing code is time consuming, you may wish to start another thread to perform the work. If the thread is still alive when the next event comes along, flag it down, and restart the operation.
Listeners and 1.1 event handling
With the 1.1 event model, you register an AdjustmentListener by calling the addAdjustmentListener() method. Then when the user moves the Scrollbar slider, the AdjustmentListener.adjustmentValueChanged() method is called through the protected Scrollbar.processAdjustmentEvent() method. Key, mouse, and focus listeners are registered through the three Component methods of addKeyListener(), addMouseListener(), and addFocusListener(), respectively. Because you need to register a separate listener for mouse events, you no longer have the problem of distinguishing between mouse events and slider events. An adjustment listener will never receive mouse events.
public void addAdjustmentListener(AdjustmentListener listener) ![]()
The addAdjustmentListener() method registers listener as an object interested in being notified when an AdjustmentEvent passes through the EventQueue with this Scrollbar as its target. The method listener.adjustmentValueChanged() is called when an event occurs. Multiple listeners can be registered.
public void removeAdjustmentListener(ItemListener listener) ![]()
The removeAdjustmentListener() method removes listener as a interested listener. If listener is not registered, nothing happens.
protected void processEvent(AWTEvent e) ![]()
The processEvent() method receives every AWTEvent with this Scrollbar as its target. processEvent() then passes it along to any listeners for processing. When you subclass Scrollbar, overriding processEvent() allows you to process all events yourself, before sending them to any listeners. In a way, overriding processEvent() is like overriding handleEvent() using the 1.0 event model.
If you override the processEvent() method, remember to call the super.processEvent(e) method last to ensure that regular event processing can occur. If you want to process your own events, it's a good idea to call enableEvents() (inherited from Component) to ensure that events are delivered even in the absence of registered listeners.
protected void processAdjustmentEven(ItemEvent e) ![]()
The processAdjustmentEvent() method receives all AdjustmentEvents with this Scrollbar as its target. processAdjustmentEvent() then passes them along to any listeners for processing. When you subclass Scrollbar, overriding processAdjustmentEvent() allows you to process all events yourself, before sending them to any listeners.
If you override processAdjustmentEvent(), you must remember to call super.processAdjustmentEvent(e) last to ensure that regular event processing can occur. If you want to process your own events, it's a good idea to call enableEvents() (inherited from Component) to ensure that events are delivered even in the absence of registered listeners.
11.2 Scrolling An Image
Example 11-1 is a Java application that displays any image in the current directory in a viewing area. The viewing area scrolls to accommodate larger images; the user can use the scrollbars or keypad keys to scroll the image. In Java 1.1, it is trivial to implement this example with a ScrollPane; however, if you're using 1.0, you don't have this luxury. Even if you're using 1.1, this example shows a lot about how to use scrollbars.
Our application uses a Dialog to select which file to display; a FilenameFilter limits the list to image files. We use a menu to let the user request a file list or exit the program. After the user picks a file, the application loads it into the display area. Figure 11-3 shows the main scrolling window.
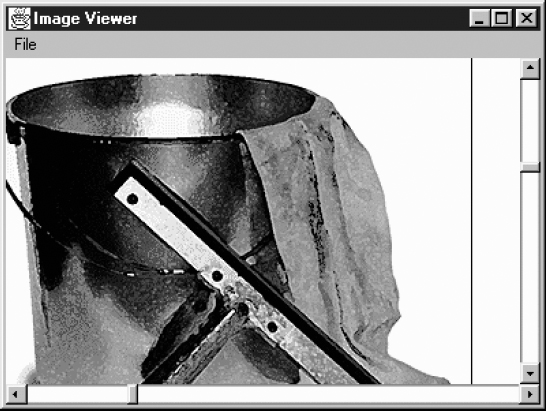
Figure 11–3: Scrolling an image
The code for the scrolling image consists of a ScrollingImage class, plus several helper classes. It places everything into the file Scrollinglmage.java for compilation.
Example 11–1: Source Code for Scrolling an Image
import java.awt.*; import java.io.FilenameFilter; import java.io.File;
The first class contains the FilenameFilter used to select relevant filenames: that is, files that are likely to contain GIF, JPEG, or XBM images. If the filename has an appropriate ending, the accept() method returns true; otherwise, it returns false.
// True for files ending in jpeg/jpg/gif/xbm
class ImageFileFilter implements FilenameFilter {
public boolean accept (File dir, String name) {
String tempname = name.toLowerCase();
return (tempname.endsWith ("jpg") || tempname.endsWith ("jpeg") ||
tempname.endsWith ("gif") || tempname.endsWith ("xbm")); } }
The ImageListDialog class displays a list of files from which the user can select. Instead of using FileDialog, we created a customized List to prevent the user from roaming around the entire hard drive; choices are limited to appropriate files in the current directory. When the user selects an entry (by double-clicking), the image is then displayed in the scrolling area.
class ImageListDialog extends Dialog {
private String name = null;
private String entries[];
private List list;
ImageListDialog (Frame f) {
super (f, "Image List", true);
File dir = new File (System.getProperty("user.dir"));
entries = dir.list (new ImageFileFilter());
list = new List (10, false);
for (int i=0;i<entries.length;i++) {
list.addItem (entries[i]);
}
add ("Center", list);
pack();
}
public String getName () {
return name;
}
public boolean action (Event e, Object o) {
name = (String)e.arg;
((ScrollingImage)getParent()).processXmage();
dispose();
return true;
}
}
The code in this class is straightforward. The constructor reads the current directory from the system property list, uses the list() method of the File class to create a list of files that match our filename filter, and then creates a List object that lists these files. getName() returns the name of the selected file. action() is called when the user selects a file; it sets the name of the selected file from the arg field of the Event and then calls the processImage() method of its parent container. The parent container of our ImageListDialog is the ScrollingImage class we are defining; its processImage() method displays a scrollable image.
The next class, ImageCanvas, is the Canvas that the image is drawn onto. We use a separate Canvas rather than drawing directly onto the Frame so that the scrollbars do not overlap the edges of the image. You will notice that the paint() method uses negative x and y values. This starts the drawing outside the Canvas area; as a result, the Canvas displays only part of the image. This is how we do the actual scrolling. (xPos, yPos) are the values given to us from the scrollbars; by positioning the image at (-xPos, -yPos), we ensure that the point (xPos, yPos) appears in the upper left corner of the canvas.
class ImageCanvas extends Canvas {
Image image;
int xPos, yPos;
public void redraw (int xPos, int yPos, Image image) {
this.xPos = xPos;
this.yPos = yPos;
this.image = image;
repaint();
}
public void paint (Graphics g) {
if (image != null)
g.drawImage (image, -xPos, -yPos, this);
}
}
ScrollingImage provides the framework for the rest of the program. It provides a menu to bring up the Dialog to choose the file, the scrollbars to scroll the scrolling canvas, and the image canvas area. This class also implements event handling methods to capture the scrollbar events, paging keys, and menu events.
public class ScrollingImage extends Frame {
static Scrollbar horizontal, vertical;
ImageCanvas center;
int xPos, yPos;
Image image;
ImageListDialog ild;
ScrollingImage () {
super ("Image Viewer");
add ("Center", center = new ImageCanvas ());
add ("South", horizontal = new Scrollbar (Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL));
add ("East", vertical = new Scrollbar (Scrollbar.VERTICAL));
Menu m = new Menu ("File", true);
m.add ("Open");
m.add ("Close");
m.add ("-");
m.add ("Quit");
MenuBar mb = new MenuBar();
mb.add (m);
setMenuBar (mb);
resize (400, 300);
}
public static void main (String args[]) {
ScrollingImage si = new ScrollingImage ();
si.show();
}
public boolean handleEvent (Event e) {
if (e.id == Event.WINDOW_DESTROY) { System.exit(0); } else if (e.target instanceof Scrollbar) { if (e.target == horizontal) { xPos = ((Integer)e.arg).intValue(); } else if (e.target == vertical) { yPos = ((Integer)e.arg).intValue(); } center.redraw (xPos, yPos, image); } return super.handleEvent (e); }
This handleEvent() method kills the program if the user used the windowing system to exit from it (WINDOW_DESTROY). More to the point, if a Scrollbar generated the event, handleEvent() figures out if it was the horizontal or vertical scrollbar, saves its value as the x or y position, and redraws the image in the new location. Finally, it calls super.handleEvent(); as we will see in the following code, other events that we care about (key events and menu events) we don't want to handle here—we would rather handle them normally, in action() and keyDown() methods.
public void processImage () {
image = getToolkit().getImage (ild.getName());
MediaTracker tracker = new MediaTracker (this);
tracker.addImage (image, 0);
try {
tracker.waitForAll();
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
xPos = 0;
yPos = 0;
int imageHeight = image.getHeight (this);
int imageWidth = image.getWidth (this);
vertical.setValues (0, 5, 0, imageHeight);
horizontal.setValues (0, 5, 0, imageWidth);
center.redraw (xPos, yPos, image);
}
processImage() reads the image's filename, calls getImage(), and sets up a MediaTracker to wait for the image to load. Once the image has loaded, it reads the height and width, and uses these to set the maximum values for the vertical and horizontal scrollbars by calling setValues(). The scrollbars' minimum and initial values are both 0. The size of the scrollbar “handle” is set to 5, rather than trying to indicate the visible portion of the image.
public boolean action (Event e, Object o) {
if (e.target instanceof MenuItem) {
if ("Open".equals (o)) {
// If showing already, do not show again
if ((ild == null) || (!ild.isShowing())) {
ild = new ImageListDialog (this); ild.show(); } } else if ("Close".equals(o)) { image = null; center.redraw (xPos, yPos, image); } else if ("Quit".equals(o)) { System.exit(0); } return true; } return false; }
action() handles menu events. If the user selected Open, it displays the dialog box that selects a file. Close redraws the canvas with a null image; Quit exits the program. If any of these events occurred, action() returns true, indicating that the event was fully handled. If any other event occurred, action() returns false, so that the system will deliver the event to any other methods that might be interested in it.
public boolean keyDown (Event e, int key) {
if (e.id == Event.KEY_ACTION) {
Scrollbar target = null;
switch (key) {
case Event.HOME:
target = vertical;
vertical.setValue(vertical.getMinimum());
break;
case Event.END:
target = vertical;
vertical.setValue(vertical.getMaximum());
break;
case Event.PGUP:
target = vertical;
vertical.setValue(vertical.getValue()
- vertical.getPageIncrement());
break;
case Event.PGDN:
target = vertical;
vertical.setValue(vertical.getValue()
+ vertical.getPageIncrement());
break;
case Event.UP:
target = vertical;
vertical.setValue(vertical.getValue()
- vertical.getLineIncrement());
break;
case Event.DOWN:
target = vertical;
vertical.setValue(vertical.getValue()
+ vertical.getLineIncrement());
break;
case Event.LEFT: target = horizontal; if (e.controlDown()) horizontal.setValue(horizontal.getValue() - horizontal.getPageIncrement()); else horizontal.setValue(horizontal.getValue() - horizontal.getLineIncrement()); break; case Event.RIGHT: target = horizontal; if (e.controlDown()) horizontal.setValue(horizontal.getValue() + horizontal.getPageIncrement()); else horizontal.setValue(horizontal.getValue() + horizontal.getLineIncrement()); break; default: return false; } Integer value = new Integer (target.getValue()); postEvent (new Event ((Object)target, Event.SCROLL_ABSOLUTE, (Object)value)); return true; } return false; } }
keyDown() isn't really necessary, but it adds a nice extension to our scrollbars: in addition to using the mouse, the user can scroll with the arrow keys. Pressing an arrow key generates a KEY_ACTION event. If we have one of these events, we check what kind of key it was, then compute a new scrollbar value, then call setValue() to set the appropriate scrollbar to this value. For example, if the user presses the page up key, we read the page increment, add it to the current value of the vertical scrollbar, and then set the vertical scrollbar accordingly. (Note that this works even though nondefault page and line increments aren't implemented correctly.) The one trick here is that we have to get the rest of the program to realize that the scrollbar values have changed. To do so, we create a new SCROLL_ABSOLUTE event, and call postEvent() to deliver it.
11.3 The Adjustable Interface
The Adjustable interface is new to Java 1.1. It provides the method signatures required for an object that lets you adjust a bounded integer value. It is currently implemented by Scrollbar and returned by two methods within ScrollPane.
11.3.1 Constants of the Adjustable Interface
There are two direction specifiers for Adjustable.
public final static int HORIZONTAL ![]()
HORIZONTAL is the constant for horizontal orientation.
public final static int VERTICAL ![]()
VERTICAL is the constant for vertical orientation.
11.3.2 Methods of the Adjustable Interface
public abstract int getOrientation () ![]()
The getOrientation() method is for returning the current orientation of the adjustable object, either Adjustable.HORIZONTAL or Adjustable.VERTICAL.
setOrientation() is not part of the interface. Not all adjustable objects need to be able to alter orientation. For example, Scrollbar instances can change their orientation, but each Adjustable instance associated with a ScrollPane has a fixed, unchangeable orientation.
public abstract int getVisibleAmount () ![]()
The getVisibleAmount() method lets you retrieve the size of the visible slider of the adjustable object.
public abstract void setVisibleAmount (int amount) ![]()
The setVisibleAmount() method lets you change the size of the visible slider to amount.
public abstract int getValue () ![]()
The getValue() method lets you retrieve the current value of the adjustable object.
public abstract void setValue (int value) ![]()
The setValue() method lets you change the value of the adjustable object to value.
public abstract int getMinimum ()
The getMinimum() method lets you retrieve the current minimum setting for the object.
public abstract void setMinimum (int minimum) ![]()
The setMinimum() method lets you change the minimum value of the adjustable object to minimum.
public abstract int getMaximum () ![]()
The getMaximum() method lets you retrieve the current maximum setting for the object.
public abstract void setMaximum (int maximum) ![]()
The setMaximum() method lets you change the maximum value of the adjustable object to maximum.
public abstract int getUnitIncrement () ![]()
The getUnitIncrement() method lets you retrieve the current line increment.
public abstract void setUnitIncrement (int amount) ![]()
The setUnitIncrement() method lets you change the line increment amount of the adjustable object to amount.
public abstract int getBlockIncrement () ![]()
The getBlockIncrement() method lets you retrieve the current page increment.
public abstract void setBlockIncrement (int amount) ![]()
The setBlockIncrement() method lets you change the paging increment amount of the adjustable object to amount.
public abstract void addAdjustmentListener(AdjustmentListener listener) ![]()
The addAdjustmentListener() method lets you register listener as an object interested in being notified when an AdjustmentEvent passes through the EventQueue with this Adjustable object as its target.
public abstract void removeAdjustmentListener(ItemListener listener) ![]()
The removeAdjustmentListener() method removes listener as a interested listener. If listener is not registered, nothing happens.
11.4 ScrollPane
A ScrollPane is a Container with built-in scrollbars that can be used to scroll its contents. In the current implementation, a ScrollPane can hold only one Component and has no layout manager. The component within a ScrollPane is always given its preferred size. While the scrollpane's inability to hold multiple components sounds like a deficiency, it isn't; there's no reason you can't put a Panel inside a ScrollPane, put as many components as you like inside the Panel, and give the Panel any layout manager you wish.
Scrolling is handled by the ScrollPane peer, so processing is extremely fast. In Example 11-1, the user moves a Scrollbar to trigger a scrolling event, and the peer sends the event to the Java program to find someone to deal with it. Once it identifies the target, it posts the event, then tries to find a handler. Eventually, the applet's handleEvent() method is called to reposition the ImageCanvas. The new position is then given to the peer, which finally redisplays the Canvas. Although most of the real work is behind the scenes, it is still happening. With ScrollPane, the peer generates and handles the event itself, which is much more efficient.
11.4.1 ScrollPane Methods
Constants
The ScrollPane class contains three constants that can be used to control its scrollbar display policy. The constants are fairly self-explanatory. The constants are used in the constructor for a ScrollPane instance.
public static final int SCROLLBARS_AS_NEEDED ![]()
SCROLLBARS_AS_NEEDED is the default scrollbar display policy. With this policy, the ScrollPane displays each scrollbar only if the Component is too large in the scrollbar's direction.
public static final int SCROLLBARS_ ALWAYS ![]()
With the SCROLLBARS_ALWAYS display policy, the ScrollPane should always display both scrollbars, whether or not they are needed.
public static final int SCROLLBARS_ NEVER ![]()
With the SCROLLBARS_NEVER display policy, the ScrollPane should never display scrollbars, even when the object is bigger than the ScrollPane's area. When using this mode, you should provide some means for the user to scroll, either through a button outside the container or by listening for events happening within the container.
Constructors
public ScrollPane () ![]()
The first constructor creates an instance of ScrollPane with the default scrollbar display policy setting, SCROLLBARS_AS_NEEDED.
public ScrollPane (int scrollbarDisplayPolicy) ![]()
The other constructor creates an instance of ScrollPane with a scrollbar setting of scrollbarDisplayPolicy. If scrollbarDisplayPolicy is not one of the class constants, this constructor throws the IllegalArgumentException run-time exception.
Layout methods
public final void setLayout(LayoutManager mgr) ![]()
The setLayout() method of ScrollPane throws an AWTError. It overrides the setLayout() method of Container to prevent you from changing a ScrollPane's layout manager.
public void doLayout () ![]()
public void layout () ![]()
The doLayout() method of ScrollPane shapes the contained object to its preferred size.
layout() is another name for this method.
public final void addImpl(Component comp, Object constraints, int index) ![]()
The addImpl() method of ScrollPane permits only one object to be added to the ScrollPane. It overides the addImpl() method of Container to enforce the ScrollPane's limitations on adding components. If index > 0, addImpl() throws the run-time exception IllegalArgumentException. If a component is already within the ScrollPane, it is removed before comp is added. The constraints parameter is ignored.
Scrolling methods
public int getScrollbarDisplayPolicy() ![]()
The getScrollbarDisplayPolicy() method retrieves the current display policy, as set by the constructor. You cannot change the policy once it has been set. The return value is one of the class constants: SCROLLBARS_AS_NEEDED, SCROLLBARS_ALWAYS, or SCROLLBARS_NEVER.
public Dimension getViewportSize() ![]()
The getViewportSize() method returns the current size of the ScrollPane, less any Insets, as a Dimension object. The size is given in pixels and has an initial value of 100 × 100.
public int getHScrollbarHeight() ![]()
The getHScrollbarHeight() method retrieves the height in pixels of a horizontal scrollbar. The value returned is without regard to the display policy; that is, you may be given a height even if the scrollbar is not displayed. This method may return 0 if the scrollbar's height cannot be calculated at this time (no peer) or if you are using the SCROLLBARS_NEVER display policy.
The width of a horizontal scrollbar is just getViewportSize().width.
public int getVScrollbarWidth() ![]()
The getVScrollbarWidth() method retrieves the width in pixels of a vertical scrollbar. The value returned is without regard to the display policy; that is, you may be given a width even if the scrollbar is not displayed. This method may return 0 if the scrollbar's width cannot be calculated at this time (no peer) or if you are using the SCROLLBARS_NEVER display policy.
The height of a vertical scrollbar is just getViewportSize().height.
public Adjustable getHAdjustable() ![]()
The getHAdjustable() method returns the adjustable object representing the horizontal scrollbar (or null if it is not present). Through the methods of Adjustable, you can get the different settings of the scrollbar.
The object that this method returns is an instance of the package private class ScrollPaneAdjustable, which implements the Adjustable interface. this class allows you to register listeners for the scrollpane's events and inquire about various properties of the pane's scrollbars. It does not let you set some scrollbar properties; the setMinimum(), setMaximum(), and setVisibleAmount() methods throw an AWTError when called.
public Adjustable getVAdjustable() ![]()
The getVAdjustable() method returns the adjustable object representing the vertical scrollbar (or null if it is not present). Through the methods of Adjustable, you can get the different settings of the scrollbar.
The object that this method returns is an instance of the package private class ScrollPaneAdjustable, which implements the Adjustable interface. this class allows you to register listeners for the scrollpane's events and inquire about various properties of the pane's scrollbars. It does not let you set some scrollbar properties; the setMinimum(), setMaximum(), and setVisibleAmount() methods throw an AWTError when called.
public void setScrollPosition(int x, int y) ![]()
This setScrollPosition() method moves the ScrollPane to the designated location if possible. The x and y arguments are scrollbar settings, which should be interpreted in terms of the minimum and maximum values given to you by the horizontal and vertical Adjustable objects (returned by the previous two methods). If the ScrollPane does not have a child component, this method throws the run-time exception NullPointerException. You can also move the ScrollPane by calling the Adjustable.setValue() method of one of the scrollpane's Adjustable objects.
public void setScrollPosition(Point p) ![]()
This setScrollPosition() method calls the previous with parameters of p.x, and p.y.
public Point getScrollPosition() ![]()
The getScrollPosition() method returns the current position of both the scrollpane's Adjustable objects as a Point. If there is no component within the ScrollPane, getScrollPosition() throws the NullPointerException runtime exception. Another way to get this information is by calling the Adjustable.getValue() method of each Adjustable object.
Miscellaneous methods
public void printComponents (Graphics g) ![]()
The printComponents() method of ScrollPane prints the single component it contains. This is done by clipping the context g to the size of the display area and calling the contained component's printAll() method.
public synchronized void addNotify () ![]()
The addNotify() method creates the ScrollPane peer. If you override this method, call super.addNotify() first, then add your customizations for the new class. You will then be able to do everything you need with the information about the newly created peer.
protected String paramString () ![]()
ScrollPane doesn't have its own toString() method; so when you call the toString() method of a ScrollPane, you are actually calling the Component.toString() method. This in turn calls paramString(), which builds the string to display. For a ScrollPane, paramString() adds the current scroll position, insets, and scrollbar display policy. For example:
java.awt.ScrollPane[scrollpane0,0,0,0x0,invalid,ScrollPosition=(0,0),
Insets=(0,0,0,0),ScrollbarDisplayPolicy=always]
11.4.2 ScrollPane Events
The ScrollPane peer deals with the scrolling events for you. It is not necessary to catch or listen for these events. As with any other Container, you can handle the 1.0 events of the object you contain or listen for 1.1 events that happen within you.
11.4.3 Using a ScrollPane
The following applet demonstrates one way to use a ScrollPane. Basically, you place the object you want to scroll in the ScrollPane by calling the add() method.
This can be a Panel with many objects on it or a Canvas with an image drawn on it. You then add as many objects as you want to the Panel or scribble on the Canvas to your heart's delight. No scrolling event handling is necessary. That is all there is to it. To make this example a little more interesting, whenever you select a button, the ScrollPane scrolls to a randomly selected position. Figure 11-4 displays the screen.
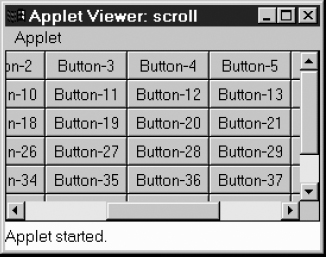
Figure 11–4: A ScrollPane containing many buttons
Here's the code:
// Java 1.1 only
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.applet.*;
public class scroll extends Applet implements ActionListener, ContainerListener {
ScrollPane sp = new ScrollPane (ScrollPane.SCROLLBARS_ALWAYS);
public void init () {
setLayout (new BorderLayout ());
Panel p = new Panel(new GridLayout (7, 8));
p.addContainerListener (this);
for (int j=0;j<50;j++)
p.add (new Button ("Button-" + j));
sp.add (p);
add (sp, "Center");
}
public void componentAdded(ContainerEvent e) {
if (e.getID() == ContainerEvent.COMPONENT_ADDED) {
if (e.getChild() instanceof Button) {
Button b = (Button)e.getChild();
b.addActionListener(this);
}
}
}
public void componentRemoved(ContainerEvent e) {
}
public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e) {
Component c = sp.getComponent();
Dimension d = c.getSize(); sp.setScrollPosition ((int)(Math.random()*d.width), (int)(Math.random()*d.height)); } }
Working with the ScrollPane itself is easy; we just create one, add a Panel to it, set the Panel's layout manager to GridLayout, and add a lot of buttons to the Panel. The applet itself is the action listener for all the buttons; when anybody clicks a button, actionPerformed() is called, which generates a new random position based on the viewport size and sets the new scrolling position accordingly by calling setScrollPosition().
The more interesting part of this applet is the way it works with buttons. Instead of directly adding a listener for each button, we add a ContainerListener to the containing panel and let it add listeners. Although this may seem like extra work here, it demonstrates how you can use container events to take actions whenever someone adds or removes a component. At first glance, you might ask why I didn't just call enableEvents(AWTEvent.CONTAINER_EVENT_MASK) and override the applet's processContainerEvent() to attach the listeners. If we were only adding our components to the applet, that would work great. Unfortunately, the applet is not notified when buttons are added to an unrelated panel. It would be notified only when the panel was added to the applet.
* MOUSE_UP, MOUSE_DOWN, and MOUSE_DRAG are not generated since these operations generate SCROLL events.
Get Java AWT Reference now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

